How to Create Jewelry Renderings with Rhino, Flamingo, and TechGems? And Aesthetic Review of Some Digital Paintings
Understanding Rhino 3D, Flamingo, TechGems and their Jewelry Design Effects
Introduction:
What if you could bring your jewelry designs to life with stunning 3D renderings? This guide shows you how to use Rhino 3D, Flamingo, and TechGems to create professional jewelry renderings. Learn why these tools are essential for jewelry designers and how to master them for creating detailed pendants, bracelets, and more. Discover the step-by-step process of using Rhino for modeling, Flamingo for rendering, and TechGems for adding realistic gemstones.

Final rendering
Table of Contents
Section I Creating Jewelry Design Renderings with Rhino
1. Learning Rhino 3D
As a professional industrial design software, Rhino is now widely used in various industries such as furniture, electronics, automotive, aerospace, and jewelry. It has become a software skill that designers in all fields must master. It is easy to learn and convenient to operate, and its principles are based on the most widely used and precise NURBS surface principles.
NURBS is an internationally recognized industrial-grade precision design standard. Its difference from polygon mesh models is that NURBS surfaces can construct models based on the curvature and size of the curve precision without excessive mesh wireframes to constrain the shape. This undoubtedly saves the number of floating-point operations and can achieve sufficiently accurate surfaces with a minimal combination of NURBS curves. NURBS surfaces can be set to a very high rendering resolution during rendering, which is different from meshes.

Rhino
NURBS surfaces of Rhino
Rhino’s User Interface
Rhino’s interface is similar to other 3D software such as 3D Studio MAX, AutoCAD, Maya, and Softimage. It is roughly divided into five areas, each serving its purpose, as shown in the table below:
Interface area of Rhino
| Interface area | Instruction |
|---|---|
| Menu | Working with Commands, Options, and Help Files |
| Toolbar | Shortcuts for using commands and options |
| Views | Displaying 3D models and 2D curves in different views in a drawing |
| Command line | Listing of executed commands and corresponding information |
| Status bar | Displaying the coordinates of input points, object status, and toggle selections |
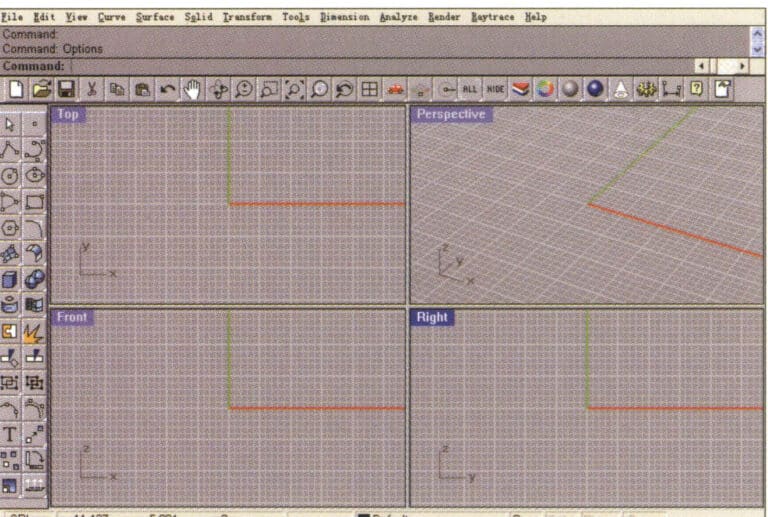
Rhino's operating interface
(1) Menu
The menu is located at the top layer of the interface, and most of Rhino’s commands are arranged as dropdown menus. To execute a command, click on the command item directly. The operation is as follows:
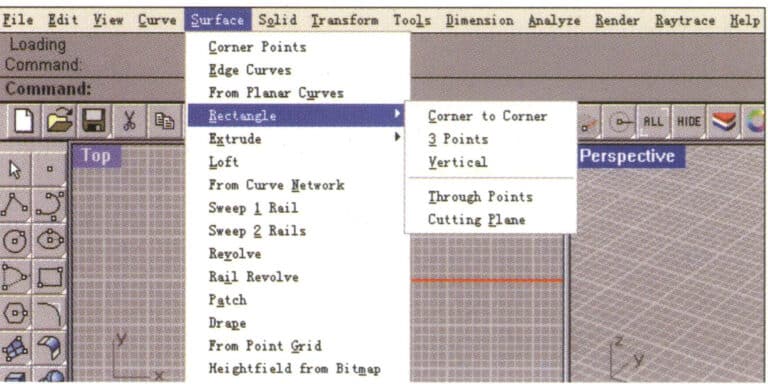
Rhino Menu
(2) Tool Bar
The tool palette in Rhino provides buttons for quickly executing commands. You can place the floating tool palette anywhere in the view or dock it at the drawing area’s edge.
When Rhino starts, it will embed the general toolbar (buttons for storage and view control, etc.) at the drawing area’s top and embed the editing toolbar (buttons for selection and copying, etc.) on the left side of the drawing area.
The tooltips’ role is to display each tool’s name and function. If you move the cursor over the tool button without moving it, a yellow tooltip will appear, showing the command’s name. Rhino has many tool buttons that can execute two commands, and the tooltip will display the shortcut keys and command names for both commands.
Many tools with dropdown tool buttons can be popped out on the toolbar. The tools on the pop-up toolbar usually belong to the same type of tool, and after clicking the mouse, the button will automatically retract.
A white triangle is at the bottom right of the pop-up tool button. To pop up the toolbar, press and hold the button with the left mouse button.

Prompt box
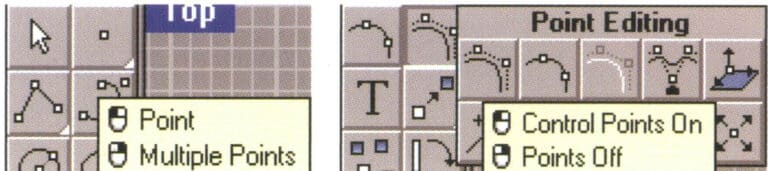
Pop-up tool button and pop-up toolbar
(3) View
The view is an area that displays the projection and perspective of the object being operated on. The default setting is four views, divided into top, front, right, and perspective. You can move or change the view size by dragging the view title bar or the edges. Each view has its own base plane and projection method. New views can be created and renamed, or the options for views can be redefined.
Double-click the view title column with the left mouse button to switch the small view to a large one, filling the entire drawing area.
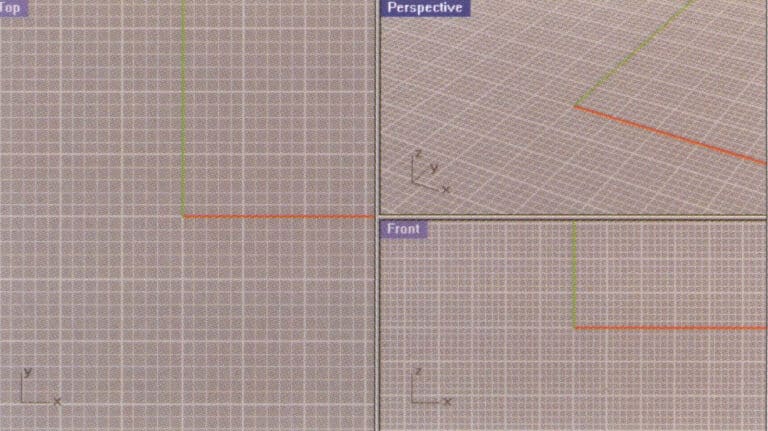
Switch the small view to the large view
(4) Command Line
The command line is the area for inputting commands or displaying the names of executed commands. It can be placed above or below the view area. The system’s default command line can display three lines of commands.
Command line
(5) State Bar
The status bar is displayed at the bottom of the interface, and its function is to show the input point coordinates, the object’s status, toggle options, etc. The status bar also has a powerful feature that allows it to snap to the current operation range, which is very helpful for accurately establishing objects.
2. Learning Flamingo
The rendering system of Rhino 3D is very limited. Compared to other 3D software like 3ds Max and Maya, rendering has become the weakest link in Rhino 3D. However, we do not need to worry about issues with Rhino’s rendering. When the official Rhino 2.0 was released, the rendering plugin Flamingo launched by AccuRender compensated for Rhino’s rendering capabilities, greatly enhancing Rhino’s rendering system, and the rendering quality was also extraordinary.
Flamingo’s rendering system is an embedded module, which we traditionally call a plugin. Flamingo can only be used when embedded into the Rhino platform, so it must be installed first. The version I am using here is Flamingo 1.0, and the left image shows the main command icons of Flamingo.
Enter the Flamingo rendering settings system. Select the Properties command from the Render menu to open the Document Properties panel, and choose the Flamingo option in the Document Properties main panel to introduce each rendering parameter.
Flamingo command icon

Renderer Flamingo

State bar
(1) Resolution Options
Viewport resolution – provides the rendering size of the actual size of the operating view, related to the actual display size of the monitor and the size of the operating window; here, it is the system’s default mode.
Custom resolution – provides manual rendering size, allowing readers to adjust the rendering size according to their requirements. The system also offers three other commonly used sizes that can be set as needed.
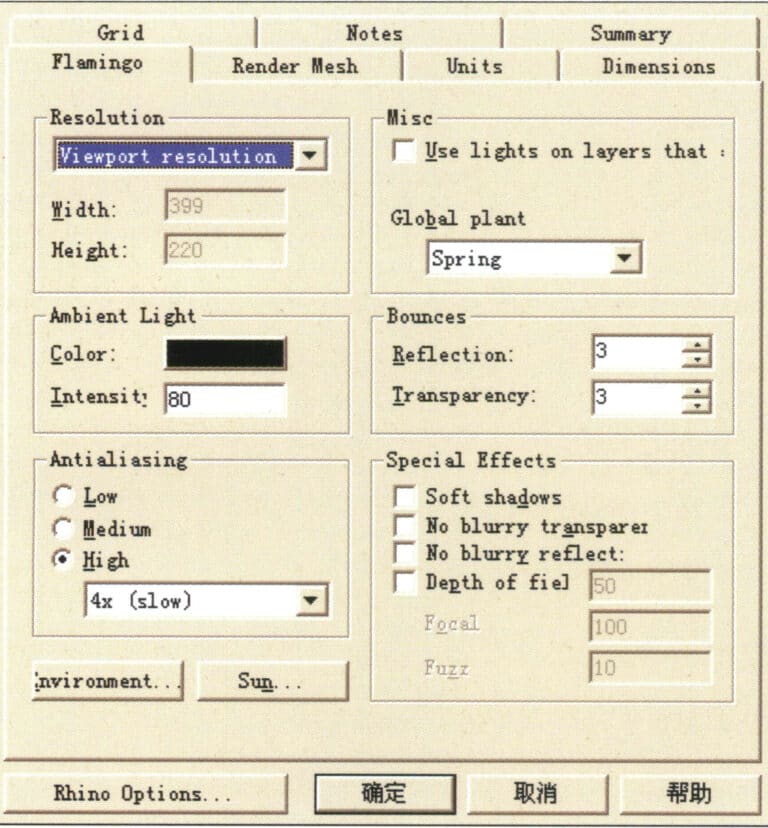
Flamingo rendering settings
(2) Misc Options
Use lights——provides built-in lighting in the system; check to turn it on.
Global Plant——global settings provide lighting for various climates.
(3) Ambient Light options
Color—-the color of light. By default, the system is set to black. Readers can adjust the corresponding color, and when the color changes, the rendering result will change according to the color of the light, as shown in below image.
Intensity—-the density of light. In simple terms, it refers to the strength of light. The system provides numerical changes; the larger the value, the stronger the color of the light. When the color of the light is black, it represents no light, and there is no change in the color and density of the light.
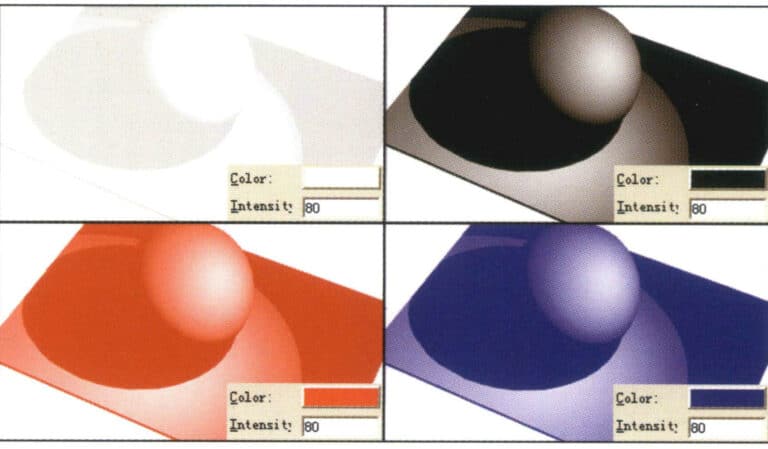
Color - The color of light
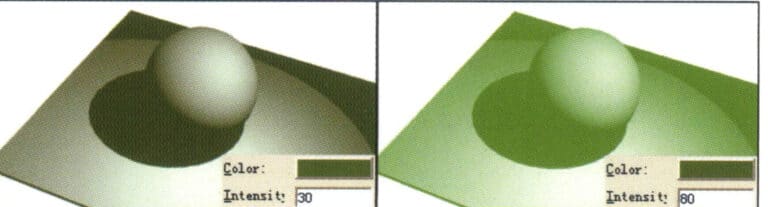
Intensity——The density of light
(4) Bounces Options
Reflection—- Reflection options. You can set the number of light reflections; the greater the refraction value of the light, the more times the light bounces within the object, which is most evident on transparent materials.
Transparency—-the number of light bounces. The higher the bounce value, the richer the colors and layers in the image, which is most evident on transparent materials. The bounce value is related to the reflection and refraction values, and the system provides manual adjustment for free control.

Bounces options
(5) Anti-aliasing Options
Low — Low anti-aliasing: Visible jagged edges in the image.
Medium — Medium anti-aliasing: Jagged edges are less noticeable.
High (4x) — High anti-aliasing (4x): Smoother edges (recommended for test rendering).
High (6x) — High anti-aliasing (6x): Smooth edges.
High (8x) — High anti-aliasing (8x): Very smooth edges (recommended for final rendering).

Antialiasing options
(6) Special Effects (Special Tools) Options:
Soft shadows: When unchecked, the shadows are hard, indicating direct lighting; when checked, the shadows are soft, indicating indirect lighting, enhancing the sense of weightlessness in the image, simulating the real shadows of objects in real life; when checked, rendering time is extended, do not enable during test rendering, please select according to requirements during final rendering.
No blurry transparent – When checked, no transparent blur is produced.
No blurry reflection – When checked, no transparent reflection is produced.
Depth of field – Depth of field option. Used to simulate the effect of reality between focus and blur. When checked, the rendering time increases geometrically; do not enable it during test rendering; please select according to requirements during final rendering.
Focal (camera focal length) – The value can be changed according to needs.
Fuzz (quality of blur) – The value can be changed according to needs.

Special Effects (Special Tools) options
(7) Environment Options
Background Color——Background Color Light Source:
Automatic Sky – Automatic Sky Light. The system customizes the skylight source, and the color of this light source cannot be modified here; it can only be changed under Ambient Light.
Solid Color (1 color light) – adjustable light source color, system default option.
2 Color Gradient (2 Colors of Light) – Provides two adjustable light source colors.
3 Color Gradient – Provides two adjustable light source colors.
(Changing the scene color can create variations in brightness and color for the scene objects; adjust as needed.)
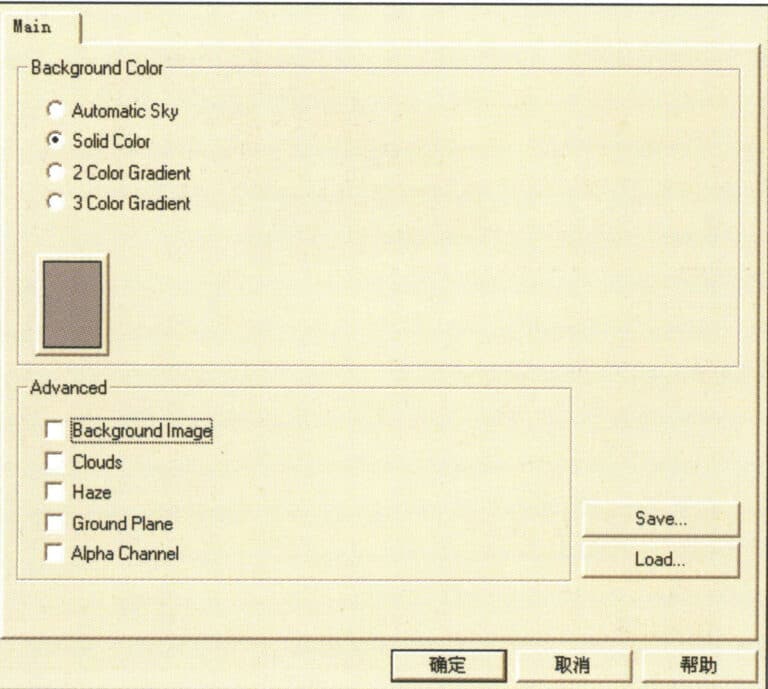
Environment options
(8) Advanced Options
Background Image — Set the image to the scene as the background image.
Clouds: Set the scene with cloud effects.
Haze – Set the scene with a smoke effect.
Ground Plane – Set the scene horizon.
(9) Flamingo’s Material Library
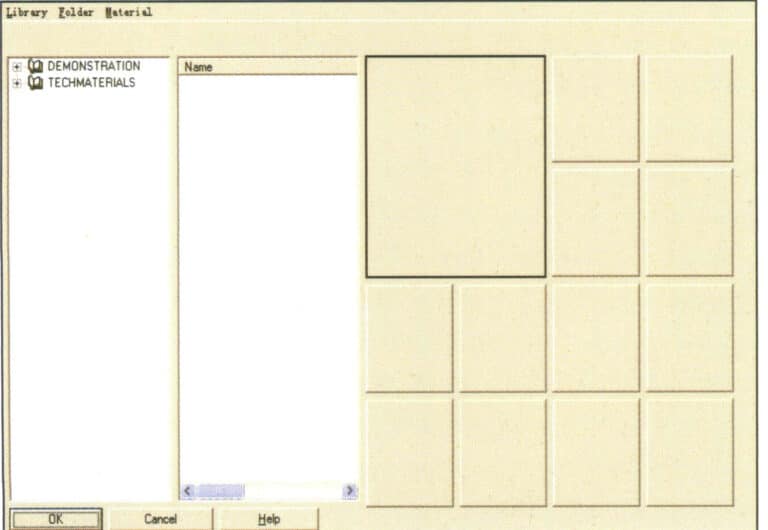
First, select the object, then choose the menu Edit > Object Properties (or click the icon in the floating tool panel) to enter the material library dialog, and select the Material option:
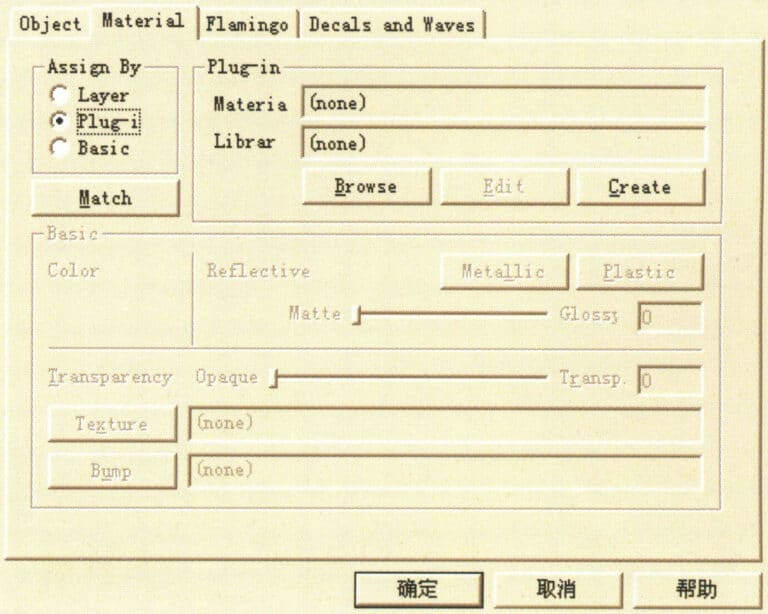
Object Properties dialog box
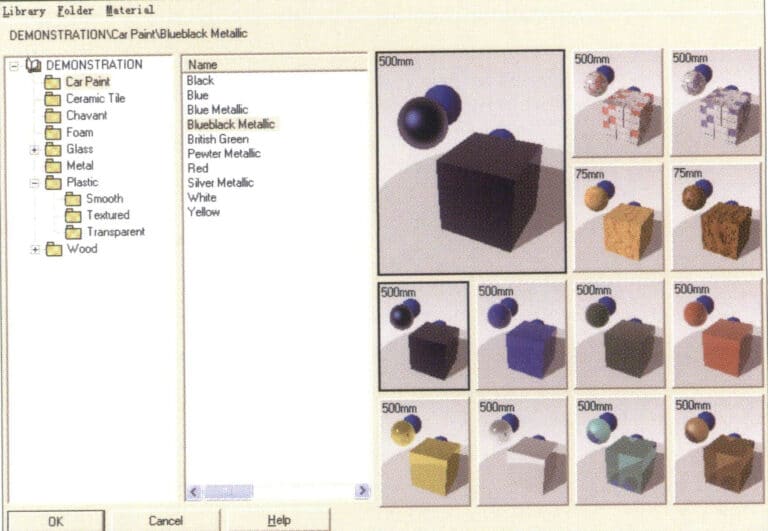
Material Library Dialog Box
The Flamingo renderer provides us with various material options, and the dropdown menu under Demonstration displays various material names. After entering the material name, the material effect appears on the right. Select the corresponding material name and click the OK button to add material properties to the selected object.
After assigning a material to the object, you can click the Edit button to enter the Flamingo Editor material dialog, which provides color settings, reflection and refraction value settings, object texture lighting properties, etc. You can adjust these as needed before confirming.
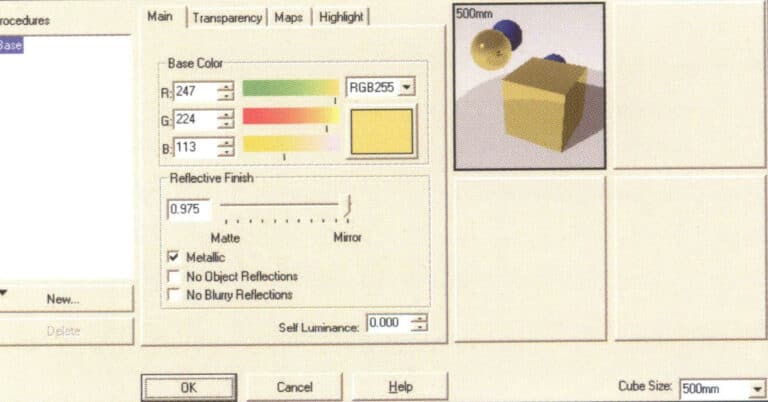
Material Editor Dialog Box
3. Learning TechGems

TechGems main module icon

TechGems
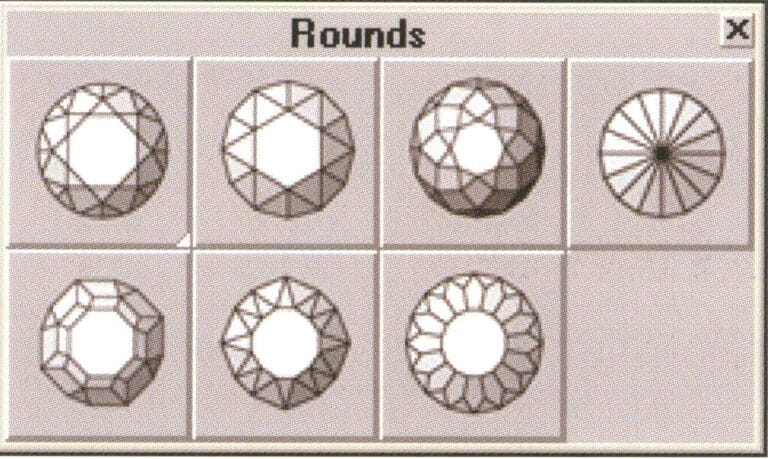
TechGems various round gemstone models
Round diamond model icon
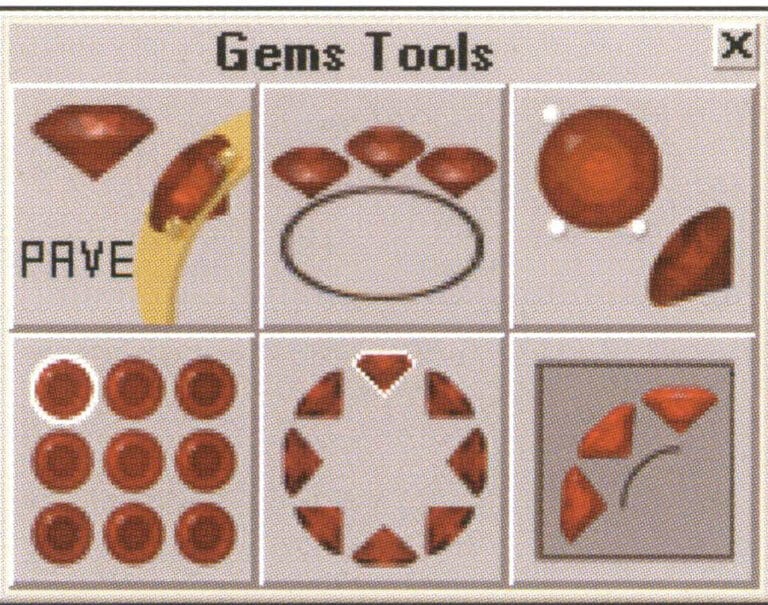
TechGems comes with six tool editing commands.
Gem Tool Icons
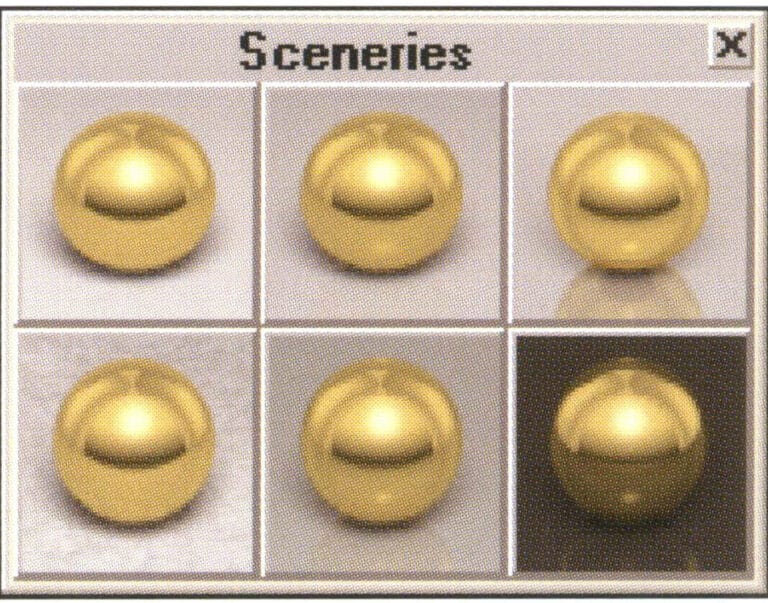
TechGems 1.1 provides six scene options.
Adjustable scene file icon
4. Rendering Jewelry Design Effects Using the Rhino Platform in Conjunction with Flamingo and TechGems
This chapter will provide a detailed step-by-step example to help readers understand how to create jewelry renderings using the Rhino platform with the Flamingo renderer and the TechGems plugin.
Open the Rhino system and open the RIO.3dm file to see the combined model of the ring. The design and modeling process is not described in this chapter, so let’s enter the world of rendering together.
Select the menu Render > Render command (or click the icon) in the floating tool panel) to pop up the rendering window. Without assigning any material to the object, the Rhino system provides a default plaster material, which, although the image quality is generally low, renders very quickly.

Object view
4.1 Endowing Objects with Metallic Texture
First, select one of the ring surfaces in the previous page’s image, then choose the command Edit > Object Properties from the menu (or click the icon in the floating tool panel to bring up the Properties dialog box).
Click the Browse button in the Plug-in section to enter the Material Library dialog box.
Expand the materials in the material library (You must install the TechGems plug-in before this material can appear. Select the Metals material category and continue to select Gold, Red Polished metal material; the material image style will appear on the right; click OK to confirm and close the dialog box.
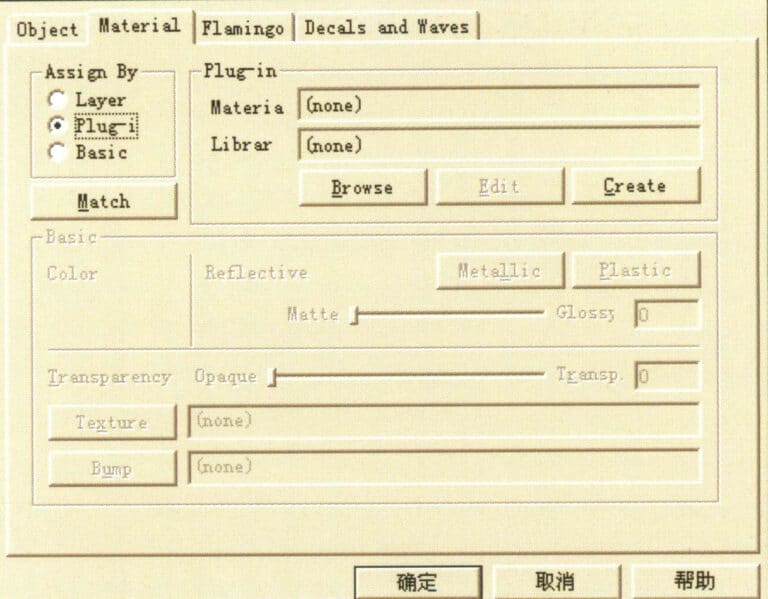
Enter Material Library
Choose other ring surfaces and apply different metal materials similarly, giving the gemstones the corresponding materials.
After material allocation, testing rendering can be performed. Click the render button to render.
The plaster material of the object itself is replaced by a metallic texture, resulting in changes in reflection and gloss on the metal surface. However, we see a large area of gray in the background of the painting because we have not yet added the scene settings.
Rhino test rendering
Flamingo test rendering
Material Library
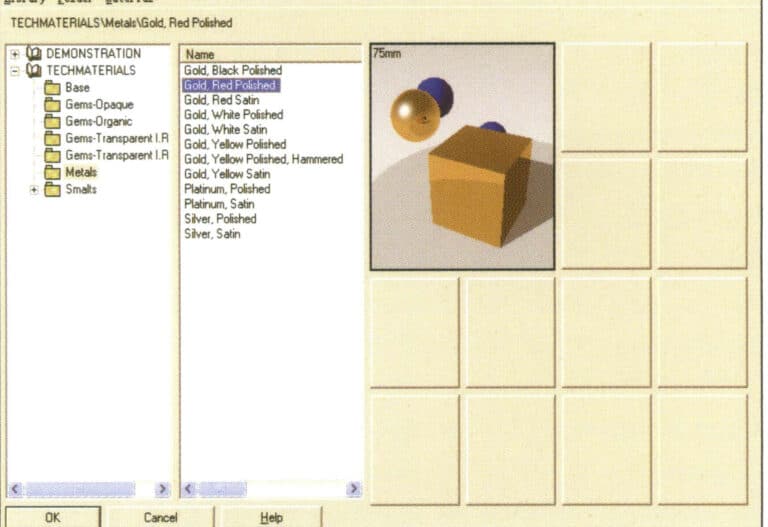
Choose the appropriate material
Gemstone material style
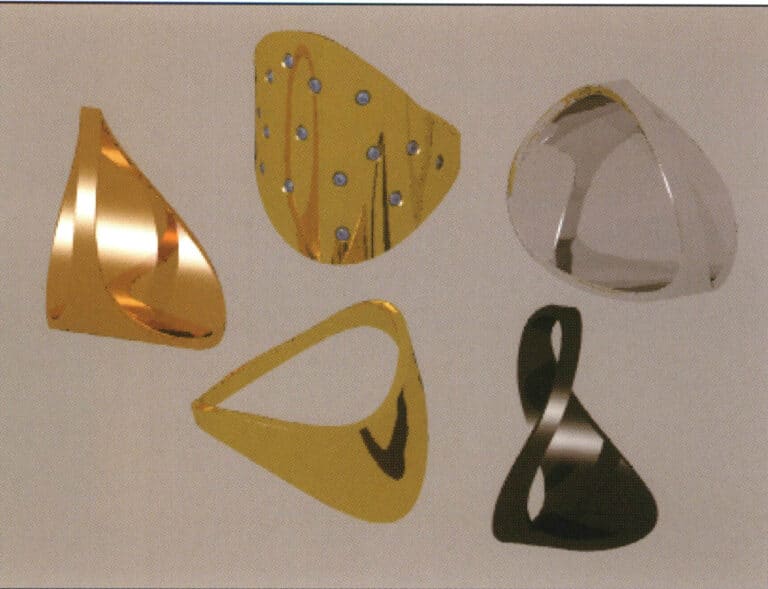

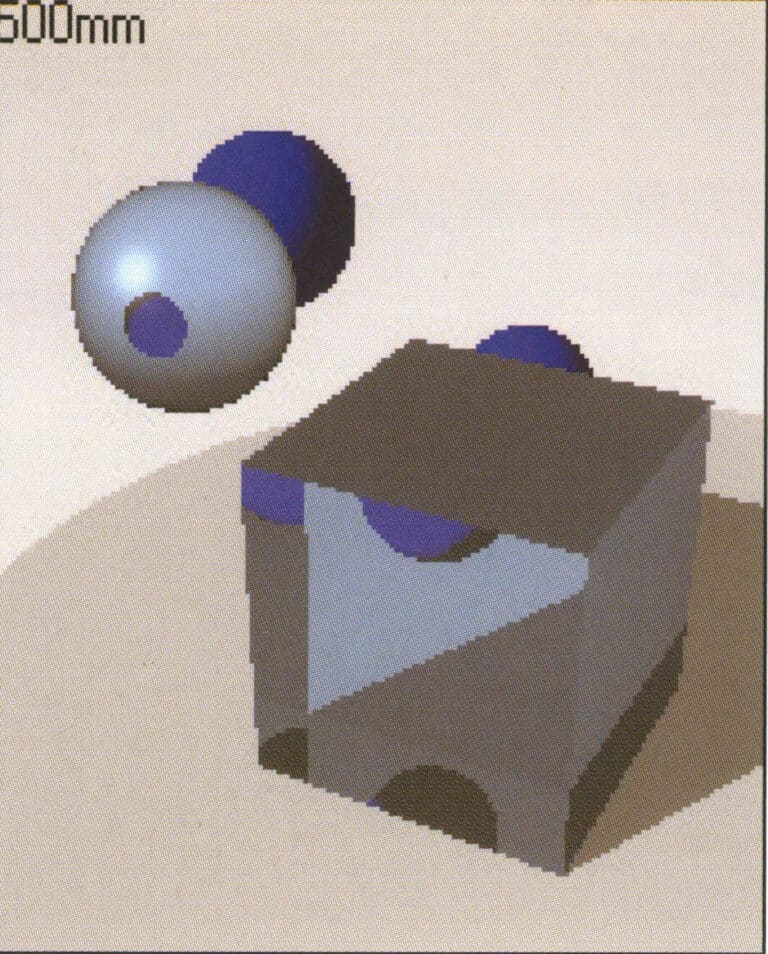
Test rendering
4.2 Setting the Scene
Select the Scenery Black Reflexive icon to import scene in the TechGems module.
The scene files provided by TechGems have already set up the corresponding scene models and lighting, and the material properties have also been configured. We need to adjust the camera angle to modify the rendering image and render again to obtain the effect.
Test rendering

Test rendering
4.3 Environmental Setup
Adding environmental settings can make the surface colors and variations of the objects richer and more layered, presenting a more realistic scene.
Enter the Environment settings of the Flamingo parameter settings in the attribute editor, select 3 Color Gradient, and adjust.
Click rendering to enrich the metallic surface of the object with light and shadow, making the changes in brightness and darkness layered; however, the object’s shadow is too strong, and the transparency of the gem has not yet been displayed, requiring further adjustment of the settings.
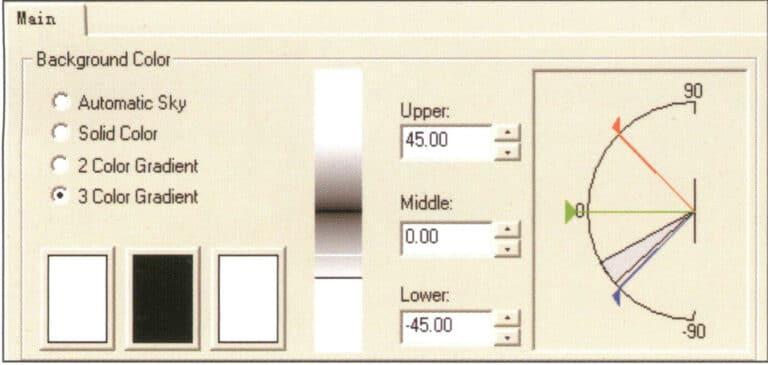
Environmental color change settings
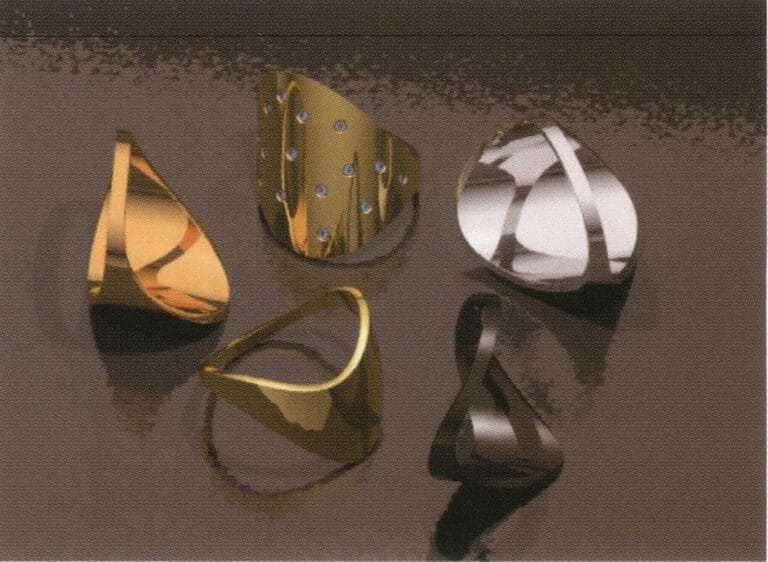

Test rendering
4.4 Adjusting the Bounces Settings
Set reflection to 12; this setting can increase the reflection value of transparent materials, making the object glossy, brighter, and richer in layers when reflecting.
Set the Transparency bounce value to 12. The larger the bounce value, the more times light refracts and reflects inside the object, resulting in richer color variations in transparent objects, thus achieving a more translucent effect.
Clicking render again, the shadows of the objects in the image are noticeably softened, making them more realistic; the color variations of the gemstones are evident, appearing more transparent; finally, after adjusting the antialiasing settings of the image, the work is complete.

Setting Reflection and Bounce Values
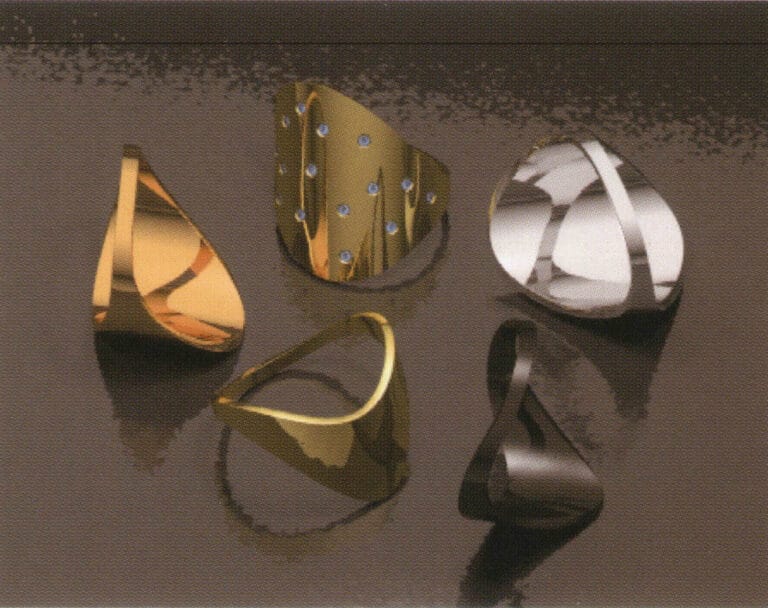

Test rendering
4.5 Setting the Antialiasing Capability and Detail Level of the Image
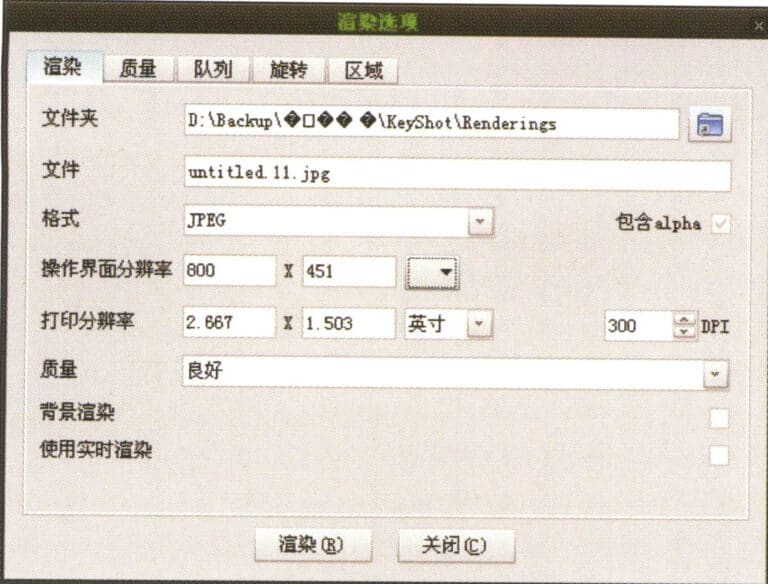
We also need to adjust the corresponding parameter settings during the final rendering. To improve the rendering quality of the image, select High > 16x (slow) in the Antialiasing options for high antialiasing capability. At this point, the rendered image’s objects, shadows, reflections, and other details will not have jagged edges, but choosing this setting will significantly extend the rendering time.
Open the Render Mesh option to set the rendering detail level, and select Smooth & slower in the Render Mesh quality section. This setting produces a more delicate image. The system also provides Custom manual parameter settings, extending the rendering time.
Finally, you can appropriately change the rendering size (adjust the corresponding height and width according to the actual aspect ratio of the image). After setting all the parameter data, you can proceed with the final rendering to obtain the final rendered effect image.
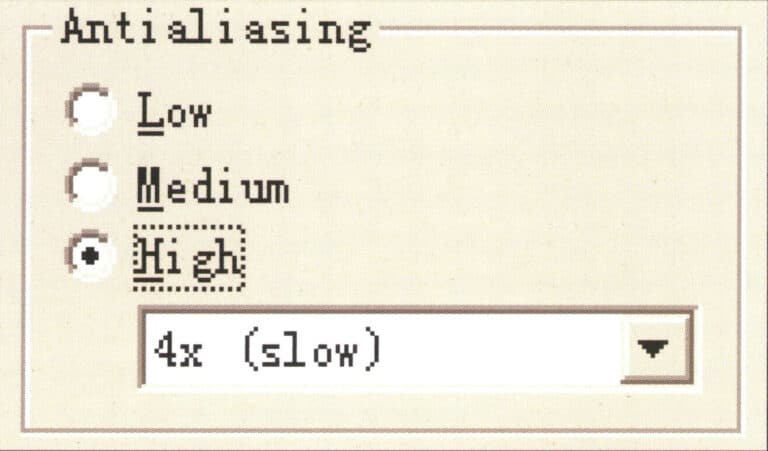
Set the antialiasing capability of the image
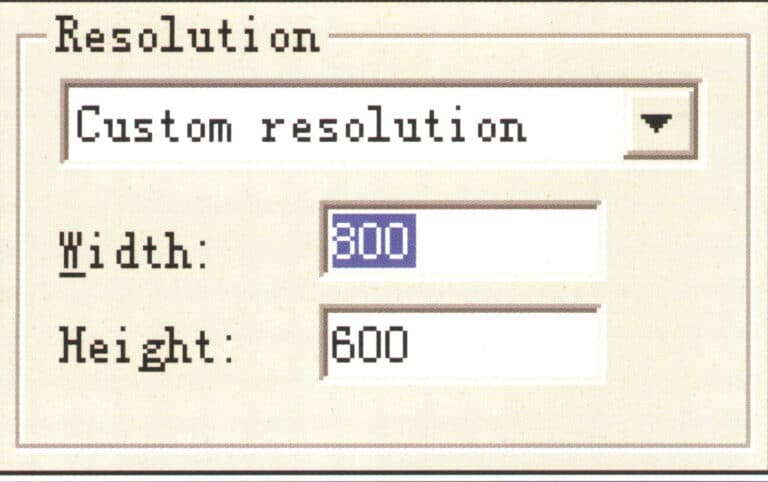
Set rendering size
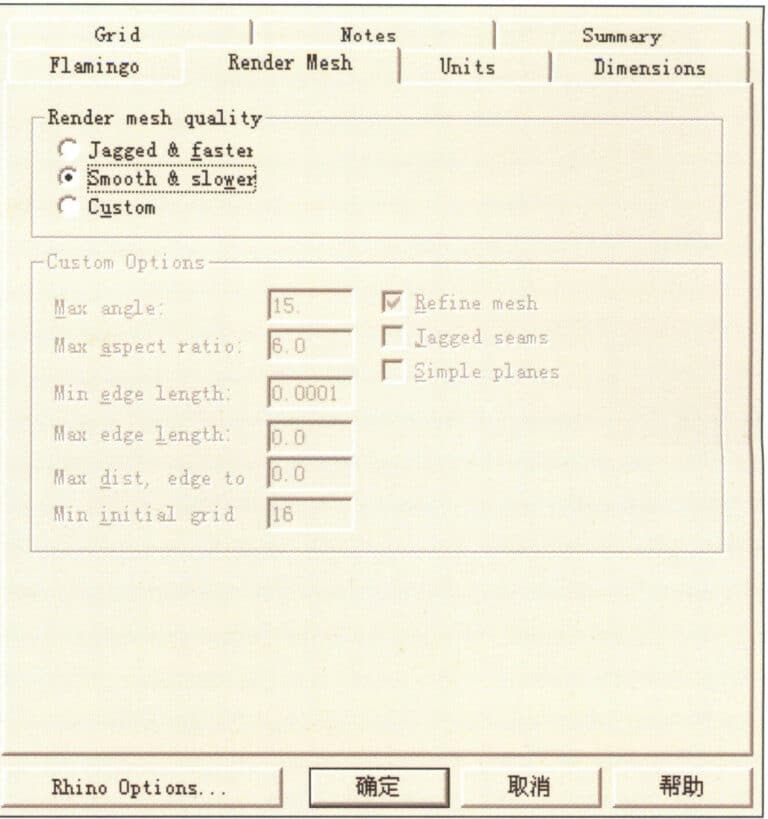
Set the smoothness parameters for the image
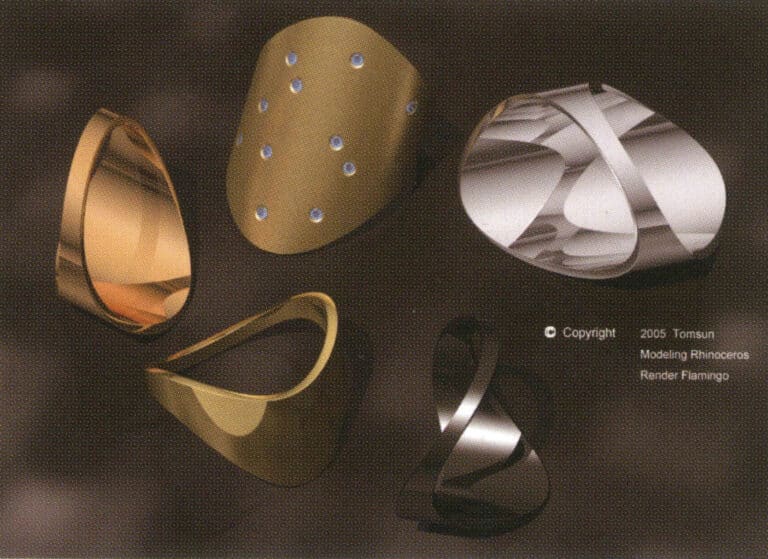

Final rendering
Copywrite @ Sobling.Jewelry — Custom jewelry manufacturer, OEM and ODM jewelry factory
5. Creating Jewelry Design Renderings with Rhino
5.1 Pendant

The steps for production are as follows:
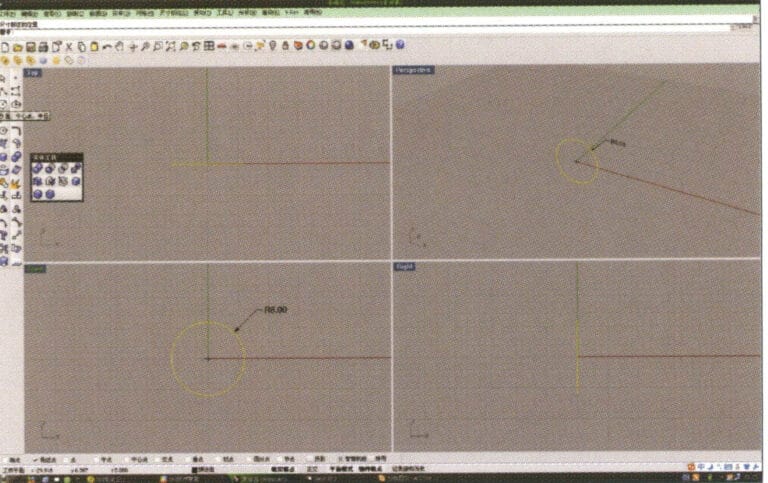
1. Open Rhino, select "Circle Tool," and draw a circular curve with a diameter of 6 mm on the Front plane

2. Select the curve that needs to be offset, long press "Curve Round Corner," then select "Offset Curve," input the required offset distance using the numeric keypad, press the stone key, and confirm.
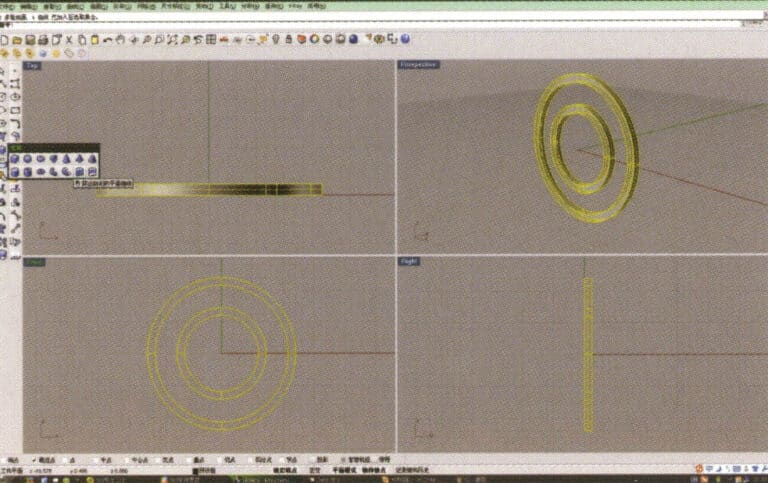
3. Select the four offset curves, long press , and choose "Solid Extrude," input the extrusion height using the numeric keypad and confirm, resulting in two ring-shaped solids
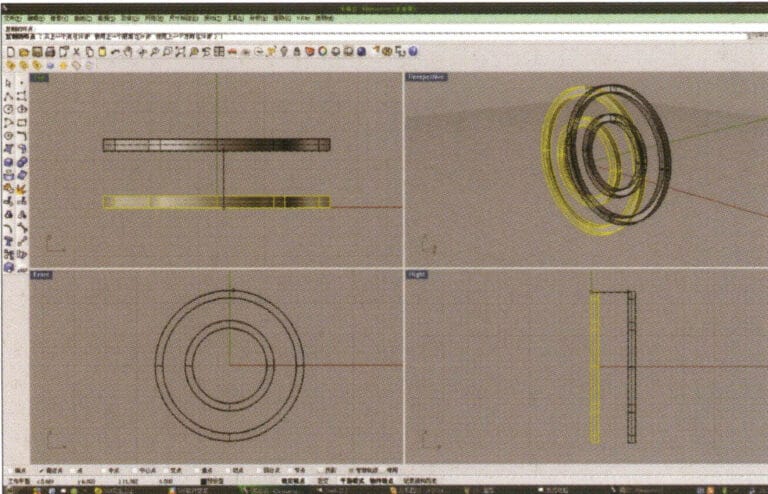
4. Select the two rings extruded in step 3, select “Duplicate”, enter the distance after duplication and confirm.
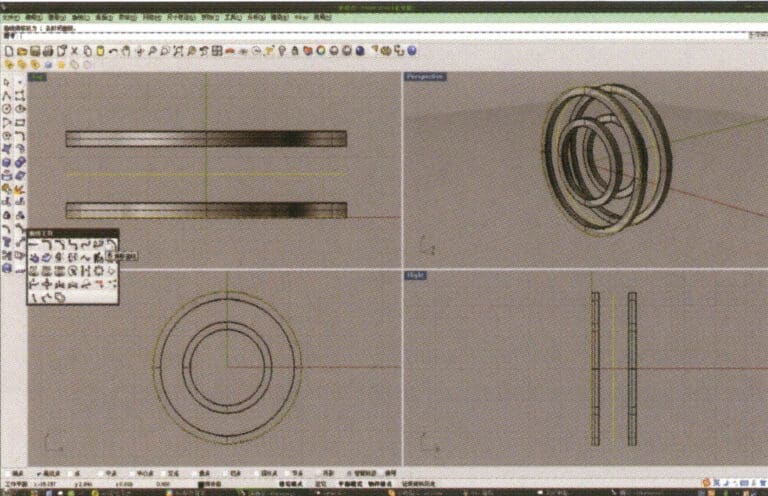
5. Select the circular curve with the largest diameter and use the "Offset Tool" to offset it to the middle of the upper and lower ring solids as a track
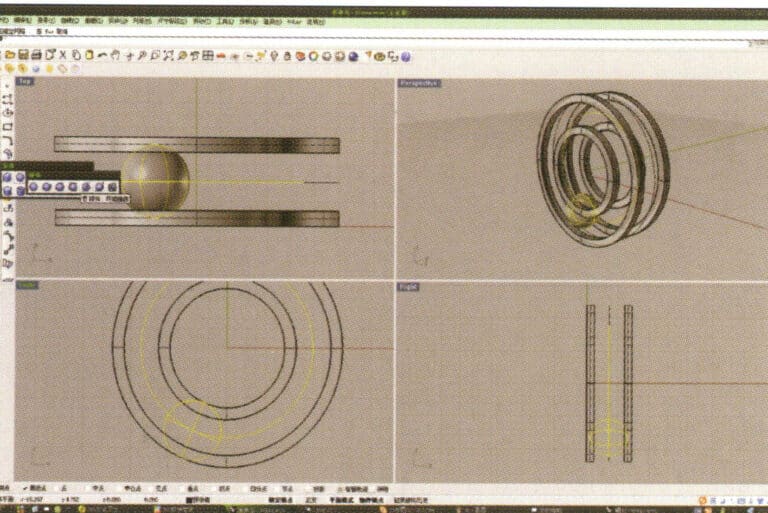
6. Select the curve as the trajectory, long press , and then long press to select "sphere, surrounding curve," check the capture command at the bottom of the window, then move the mouse to the desired drawing location, click the left button to confirm the position of the center, and then enter the radius of the sphere. After confirmation, the sphere is obtained
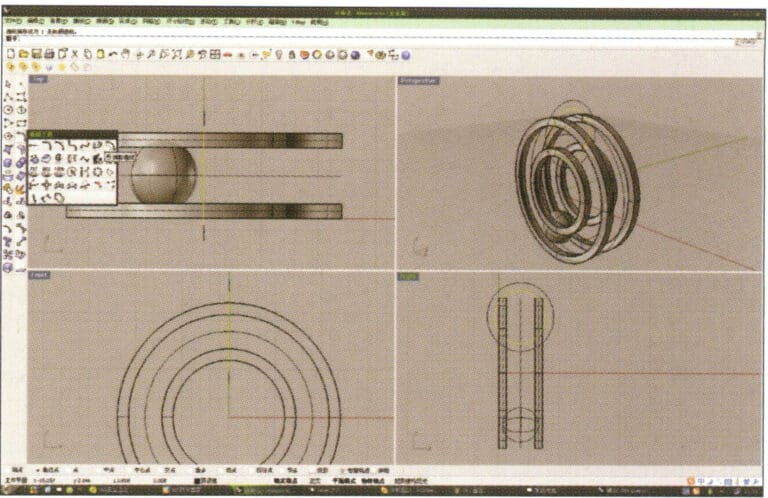
7. Similar to step 6, select the trajectory curve, long press , and choose "ring curve." Move the mouse to the center of the circle and enter the radius as prompted in the prompt bar to obtain the first ring curve, then select "offset" to get the second curve
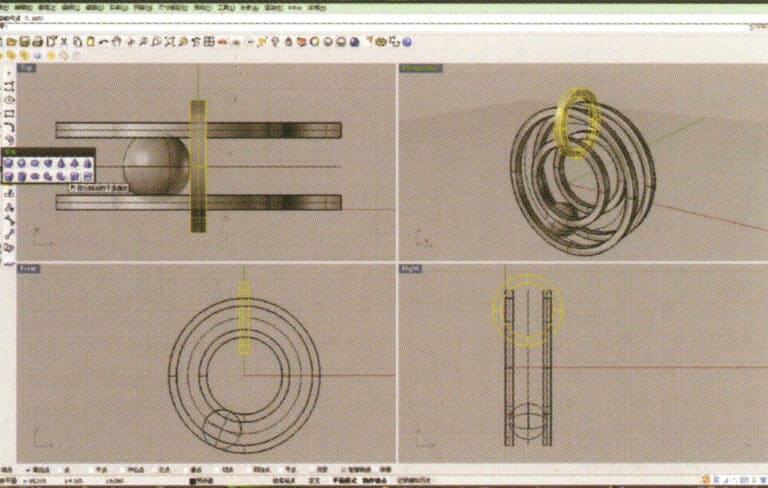
8. Select the two circular curves obtained in step 7, long press , and choose "Extrude," input the extrusion height using the numeric keypad and confirm while moving the circular solid to the center
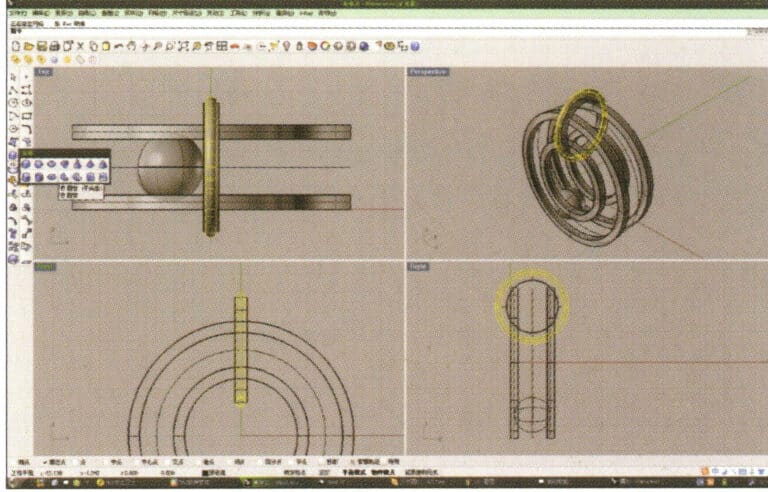
9. Select the previously created outer circular curve as the track, and choose tube to create a circular tube
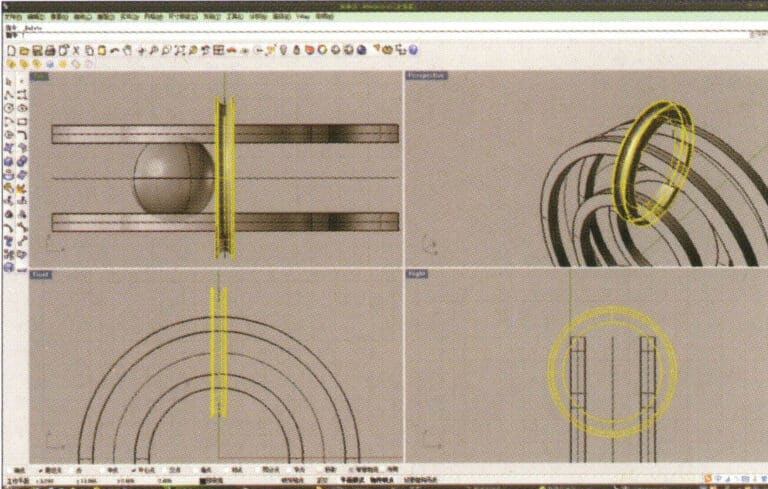
10. First select the ring-shaped solid, then choose "Boolean operation difference," and then select the circular tube and confirm
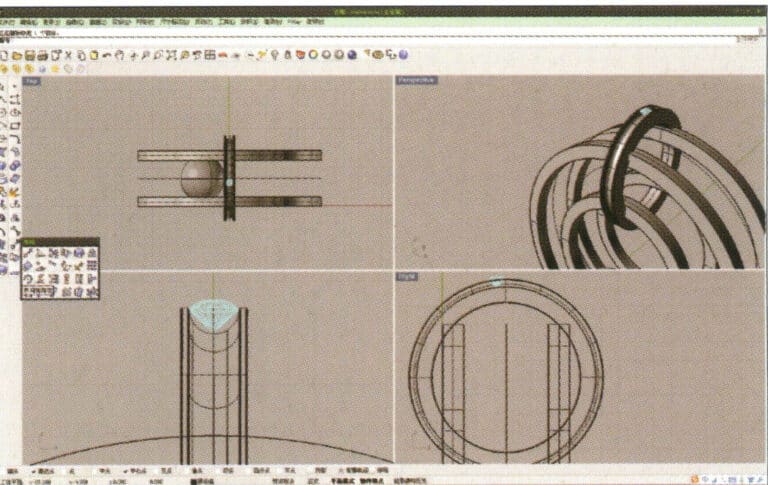
11. Import the diamond model and move it directly above the groove created in step 10
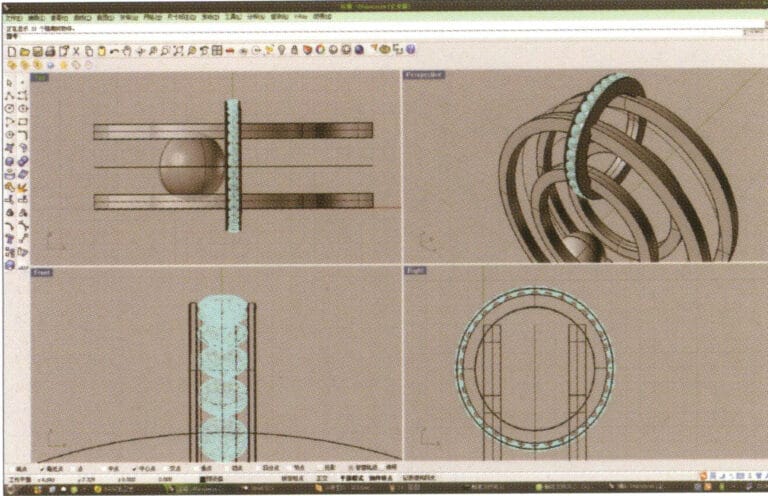
12. Select the diamond, long press , and choose "Circular Array," then follow the instructions in the prompt bar at the top of the window to enter the number of arrays and confirm
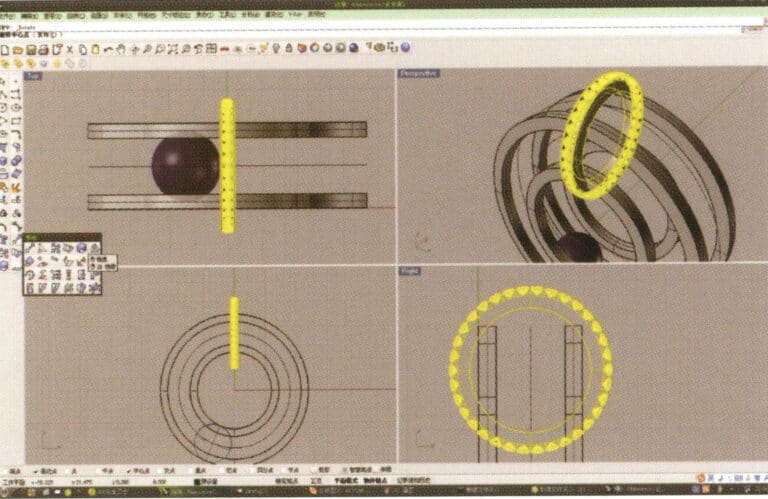
13. Select the annular surface and diamond obtained in step 12, and long press

14. Select "Mirror" for the chives, check the "Capture Command - Center Point" at the bottom of the window, and after determining the center point, perform the mirror operation using that center point
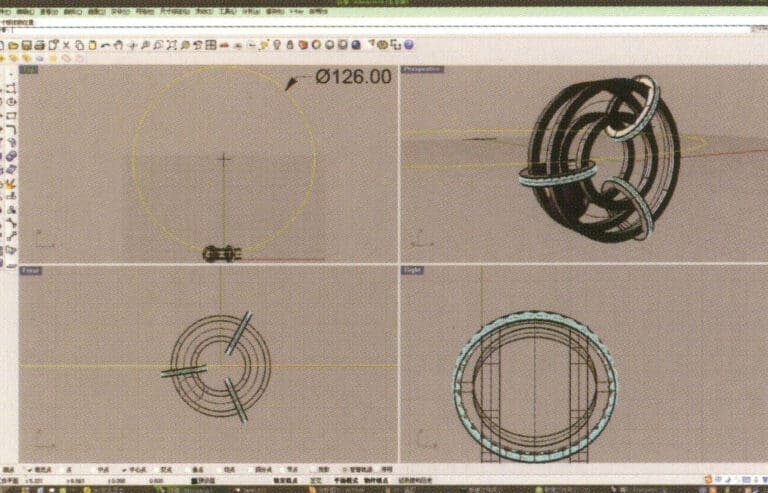
15. Select "Circle Tool" and draw a circular curve with a diameter of 126 mm on the Top plane
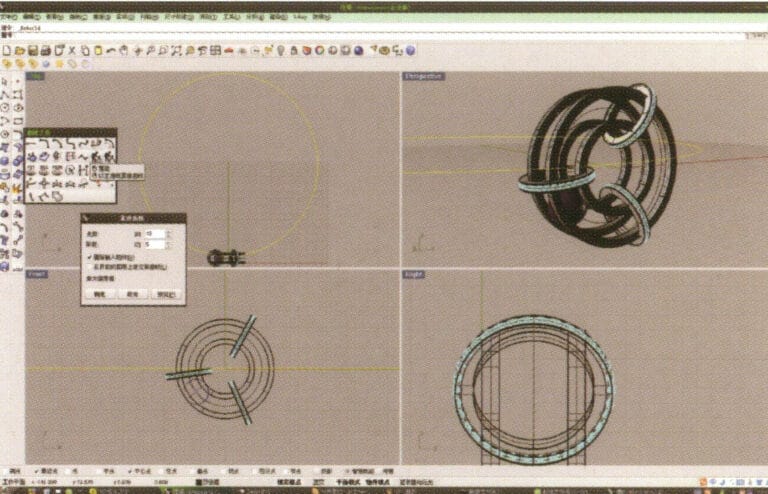
16. Select the curve obtained in step 14, choose "Rebuild," enter 10 in "Point Count," enter 5 in "Degree," and confirm
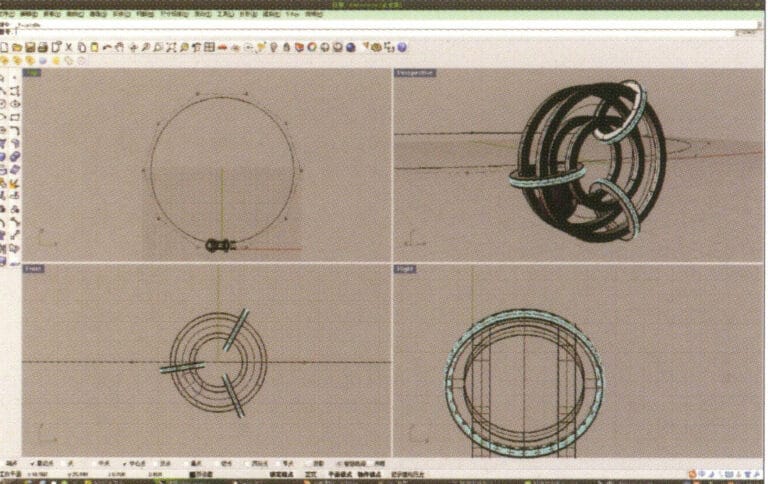
17. After confirmation, select the curve and press "F10" to display the 10 control points created earlier
18. By selecting and moving control points, deform the curve and make it pass through the two small rings
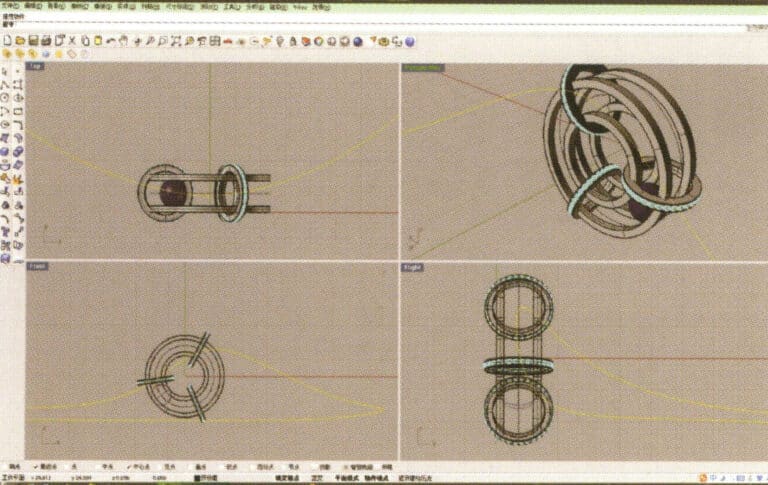
19. Choose the deformed curve as the track, and select "circular tube" to create a radius of 0.5 round tube
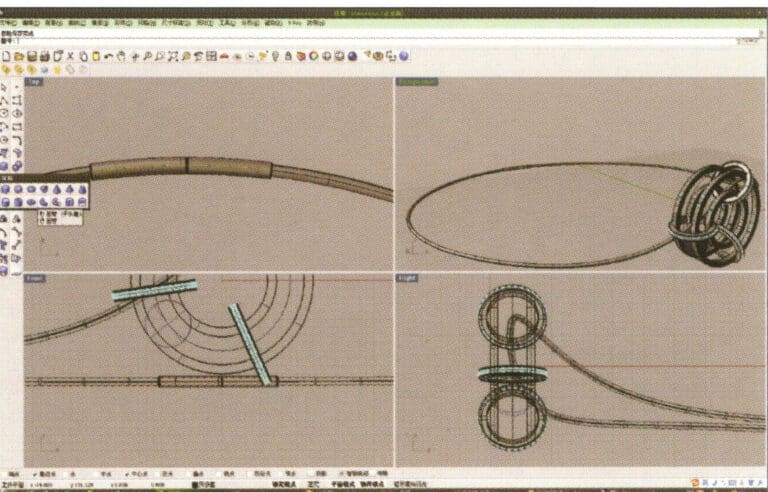
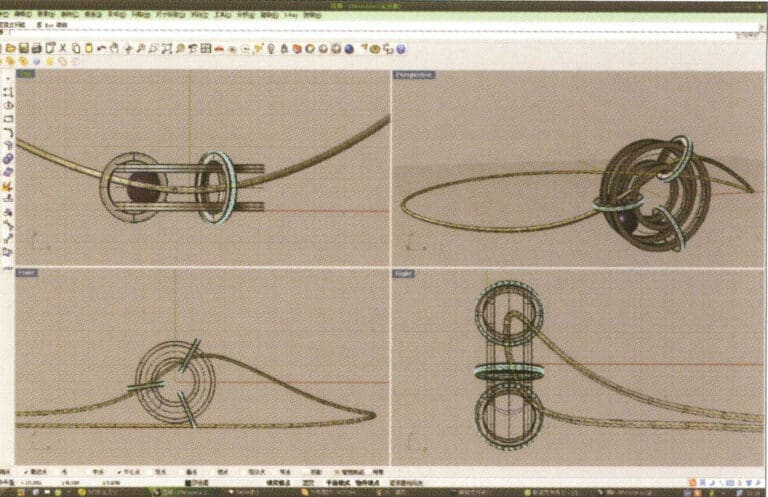
20. Use the same method as in step 18 to add details to the chain

21. Select separately, first create a new layer in the "Layers" window on the right, then select the parts with the same material in the model, choose color layering in the "Layers" section of the "Properties" window, complete and save
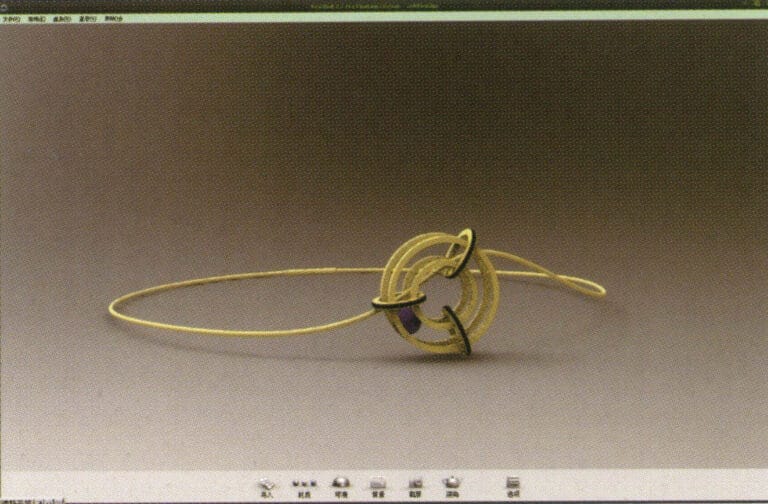
22. Select "rendering software" for rendering, and after opening, directly drag the "Rhino model" into the Keyshot workspace
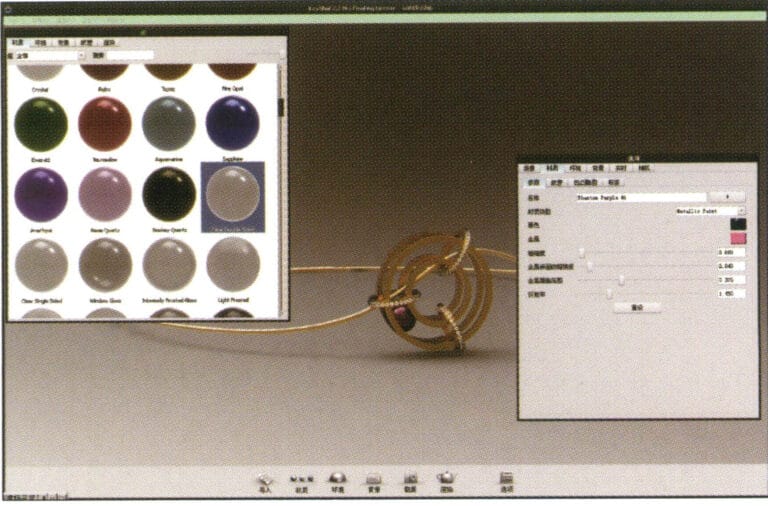
23. Open the "Material" library, select the desired material, and drag it directly onto the corresponding model part to start applying it. After completion, you can double-click the model to adjust the details of that part's material
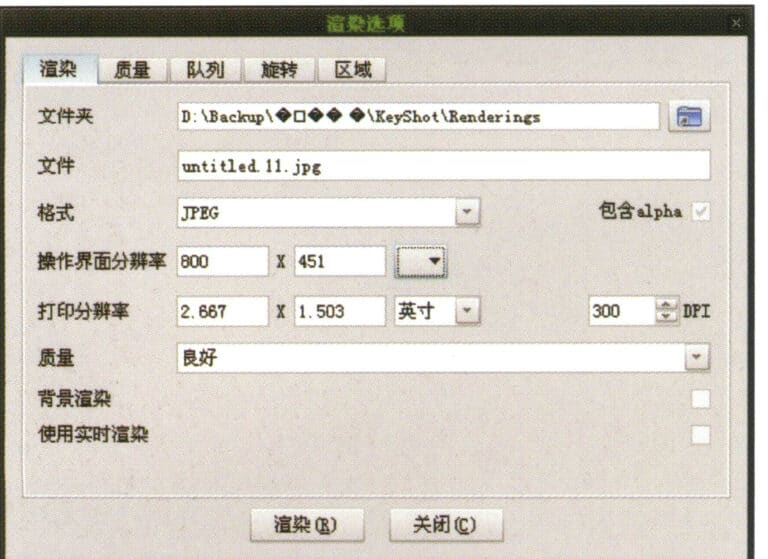
24. After adjusting the material, environment, and view, you can select "Render" to adjust the rendering quality
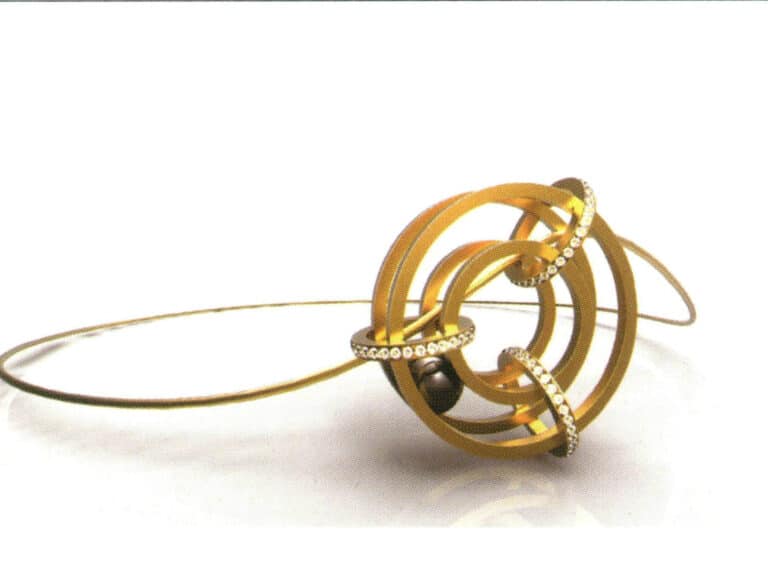

25. Rendering completed
5.2 Bracelet
The steps for production are as follows:
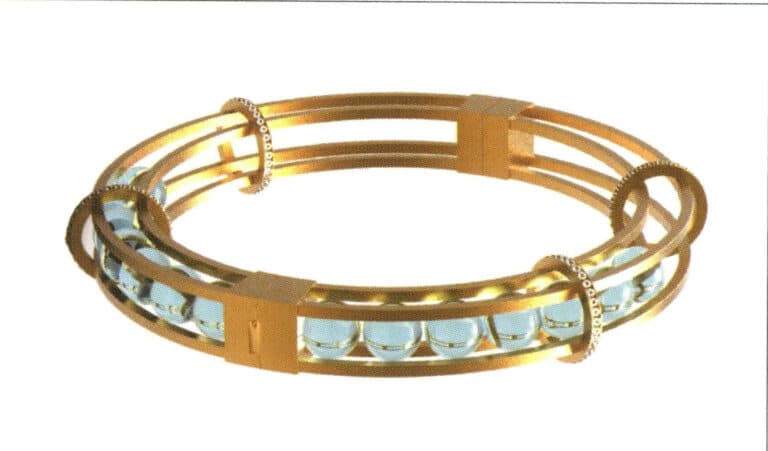

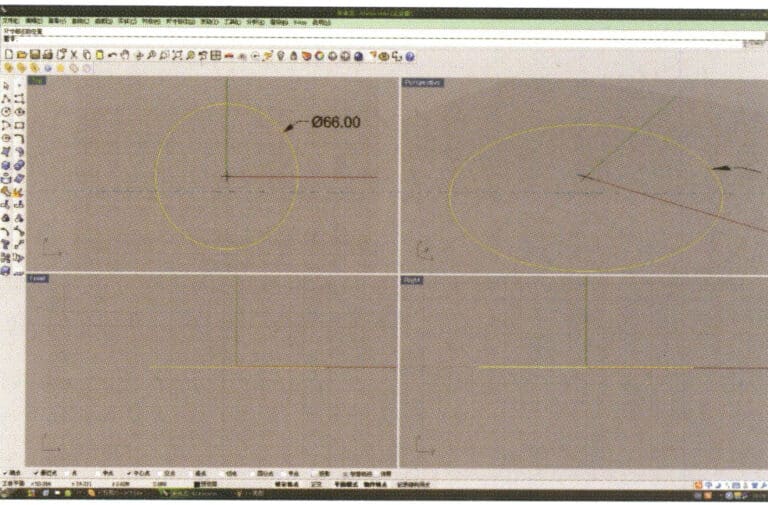
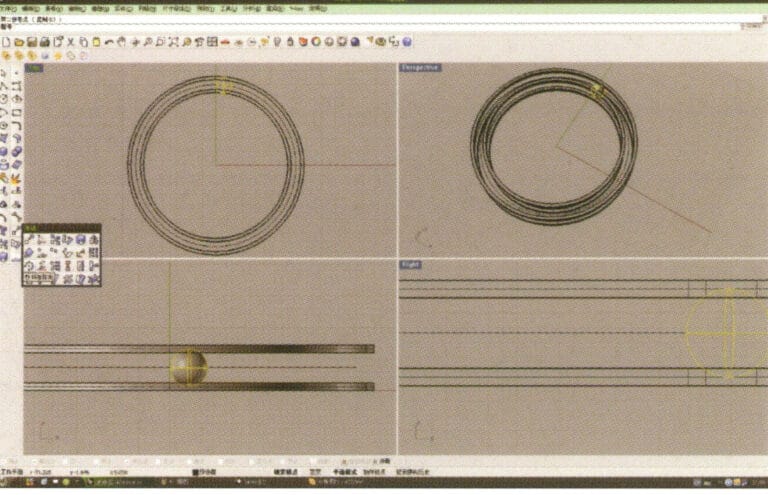
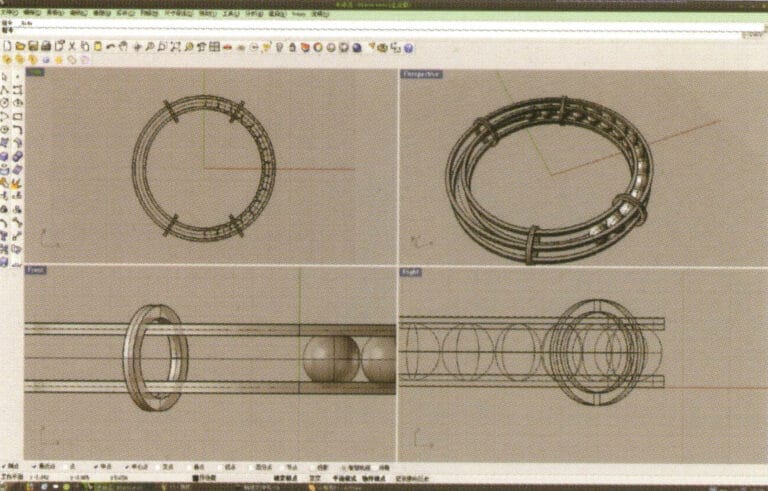
1. Open Rhino, select the "Circle Tool" and draw a circular curve with a diameter of 66 mm on the Top plane
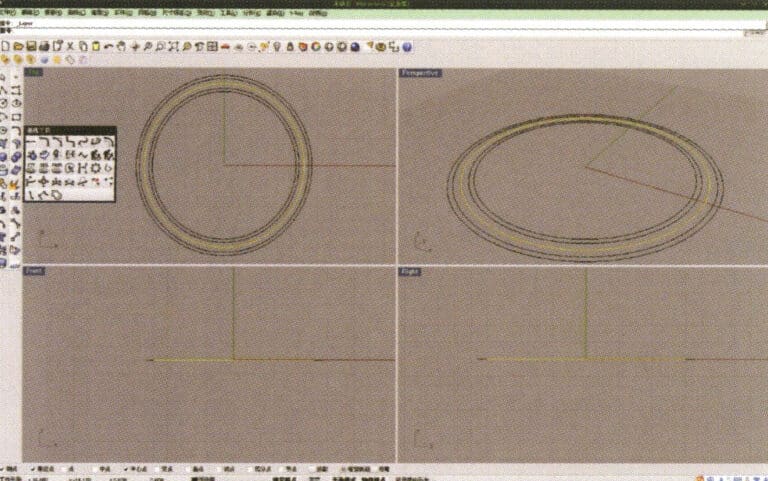
2. Select the curve that needs to be offset, long press "Curve Round Corner," then select "Offset Curve," input the required offset distance using the small keyboard, right-click, and confirm that the yellow curve in the image serves as the trajectory for the subsequent array of spheres
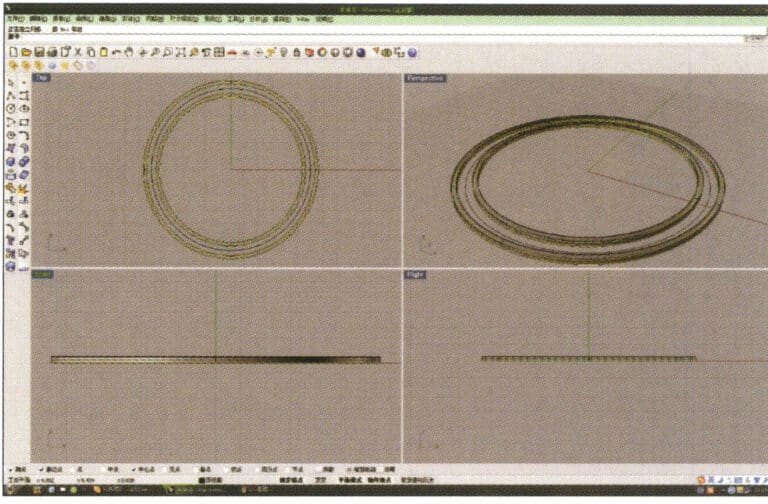
3. Select the two sets of curves to be extruded, long press and choose "Extrude," then enter the extrusion height using the numeric keypad and confirm

4. Select the two extruded surfaces from step 3, choose "Copy," enter the distance for the copy, and confirm; then select the curve used as the trajectory in step 2, and choose "Move" to move it up to the middle position between the two surfaces.
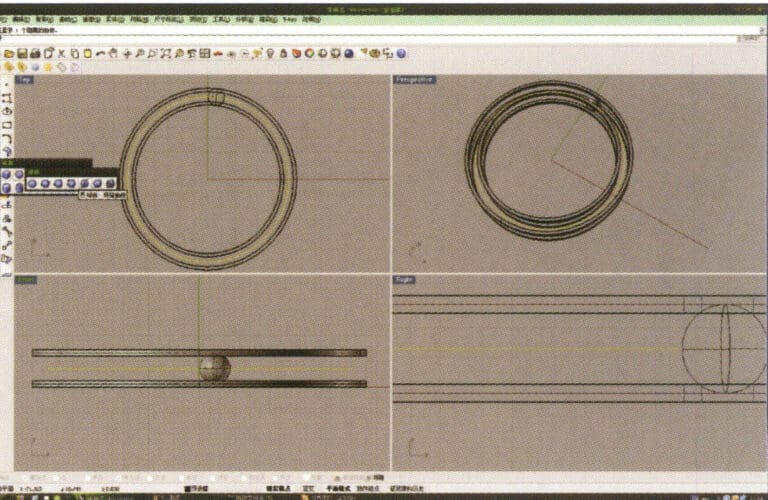
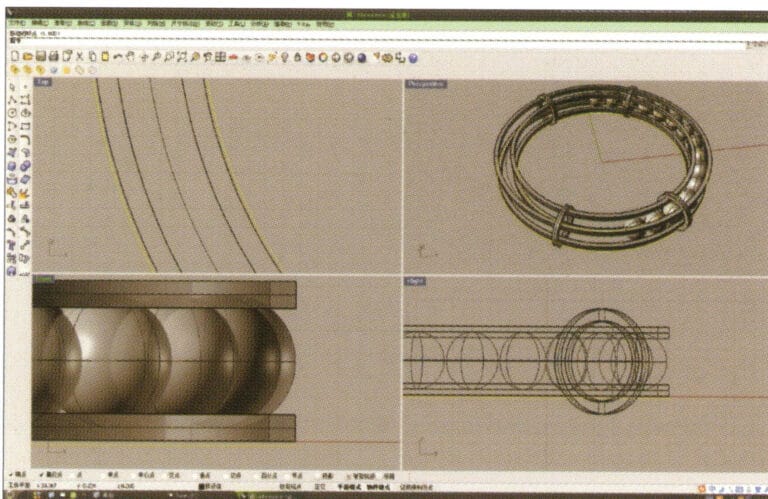
5. Select the curve as the trajectory, long press and then long press to select "sphere, surrounding curve," check the capture command "nearest point" below the window, then move the mouse to the location where you need to draw, click the left mouse button to confirm the position of the center of the sphere, then input the radius of the sphere, and after confirmation, obtain the sphere
6. Select the sphere, long press and then select “Circular array”, and then follow the instructions in the prompt bar above the window, enter the number of arrays and confirm
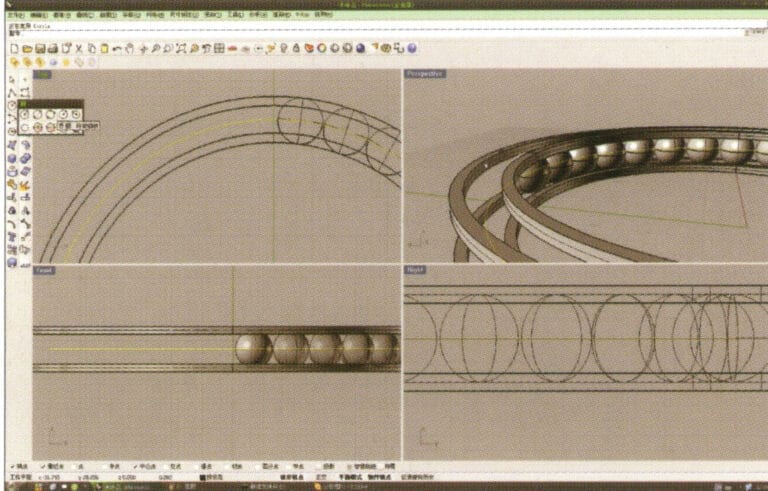
7. Similar to step 5, select the trajectory curve, long press , and then choose "ring curve." Move the mouse to the center of the circle and enter the radius as prompted in the prompt bar to obtain the first circular curve, then use "offset" to get the second curve
8. Select the two circular curves obtained in step 7, long press , and choose "Solid Extrude," enter the extrusion height using the numeric keypad and confirm
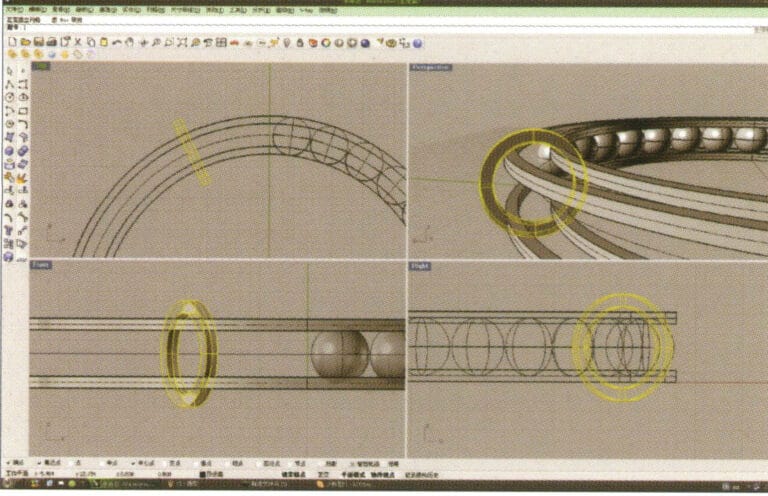
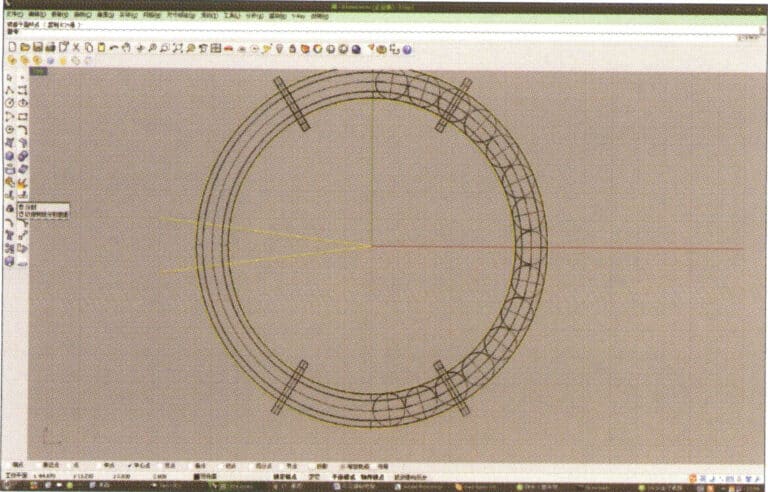
9. Select the annular surface obtained in step 8, long press then select "mirror."
10. Check the capture command for the center point below the selection window, and after determining the center point, use it for the mirroring operation
11. Select the outermost and innermost curves established initially and offset them one by one to obtain two new annular curves
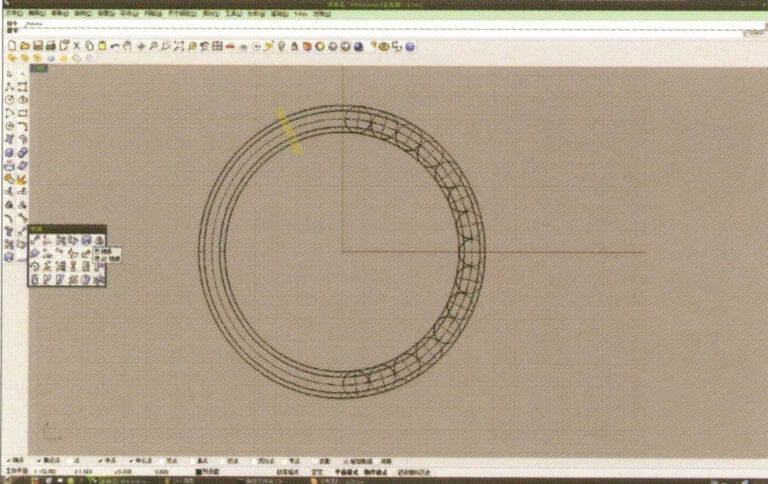
12. Create two straight lines, use "Split" to cut the two rings, and after completing that, use the resulting arcs to cut the two straight lines to obtain curves, then select and run to convert them into closed curves
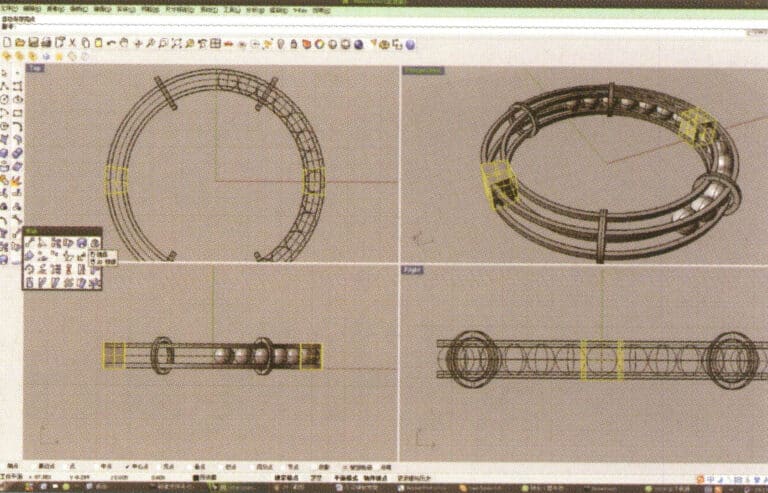
13. Select the closed curve obtained in step 12 and extrude it, then mirror it
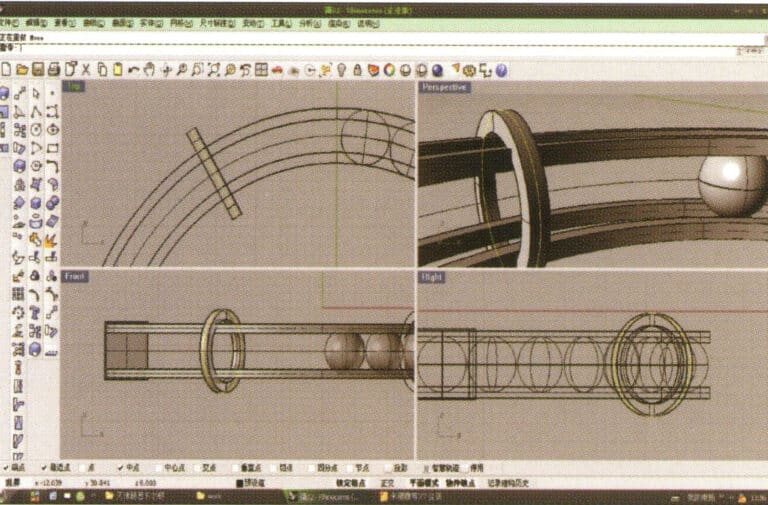
14. Select the edge curve of the circular solid, and choose "Offset Curve" to offset it to the center as the trajectory curve
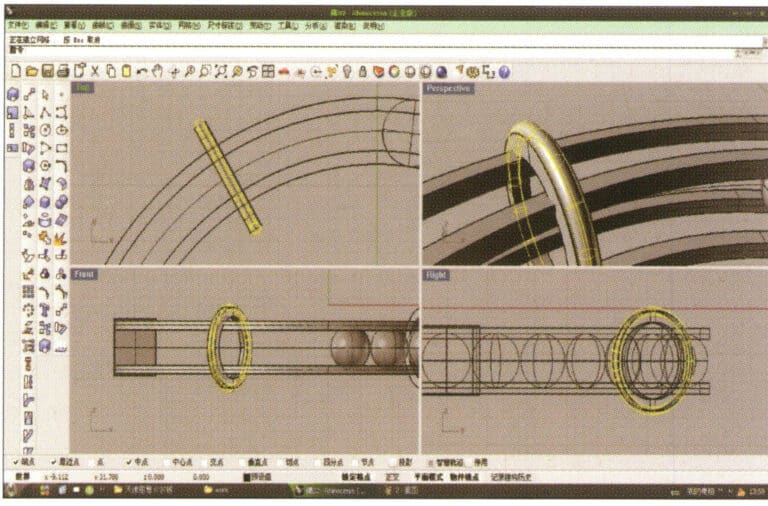
15. Long press to select "cylindrical tube," input the radius to obtain the cylindrical tube
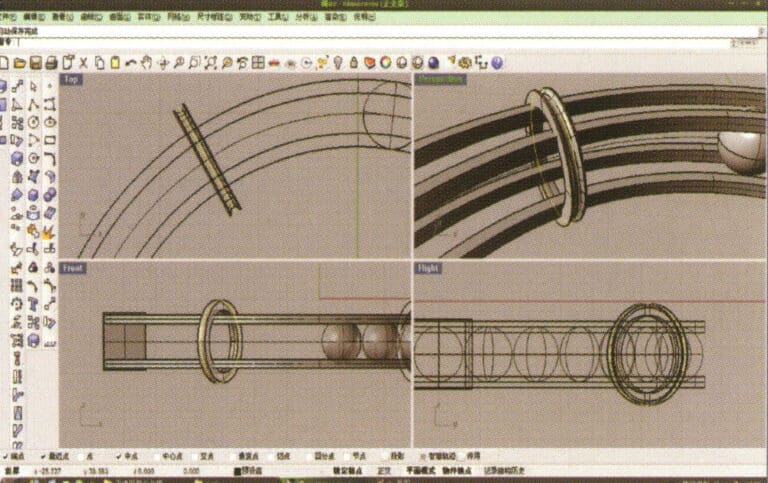
16. Select the small ring solid, long press to select "Boolean operation difference," then select the circular tube obtained in step 15, right-click and confirm (ring solid minus circular tube)
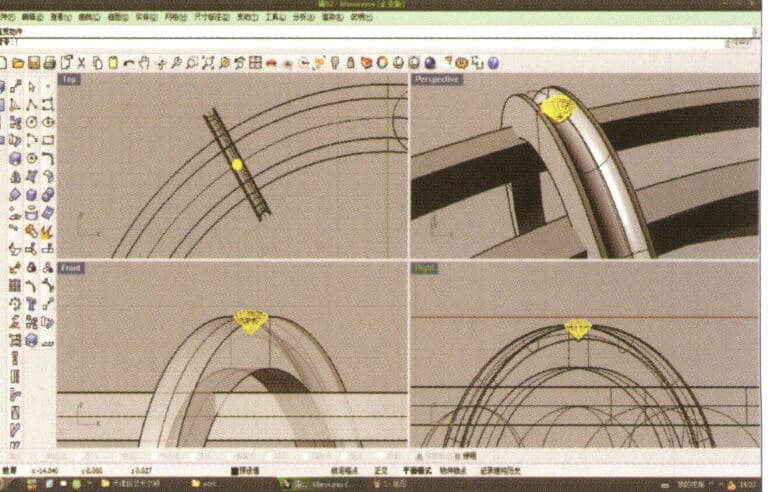
17. Import the diamond model and move it directly above the groove created in step 16
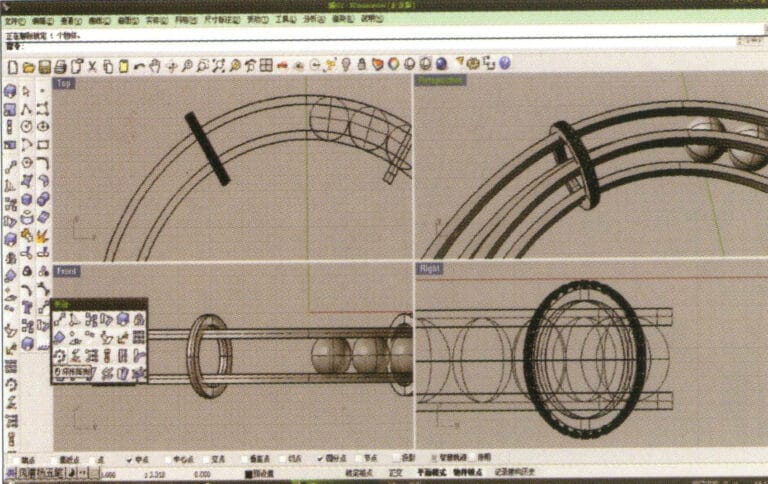
18. Select the diamond, then choose the "Circular Array Tool," and follow the prompts in the hint bar at the top of the window to input the number of arrays and confirm
19. Hold down "Shift," select all the diamonds after the array, and use the "Mirror Tool" with the center point as the center to mirror the diamonds into the other three ring-shaped entities
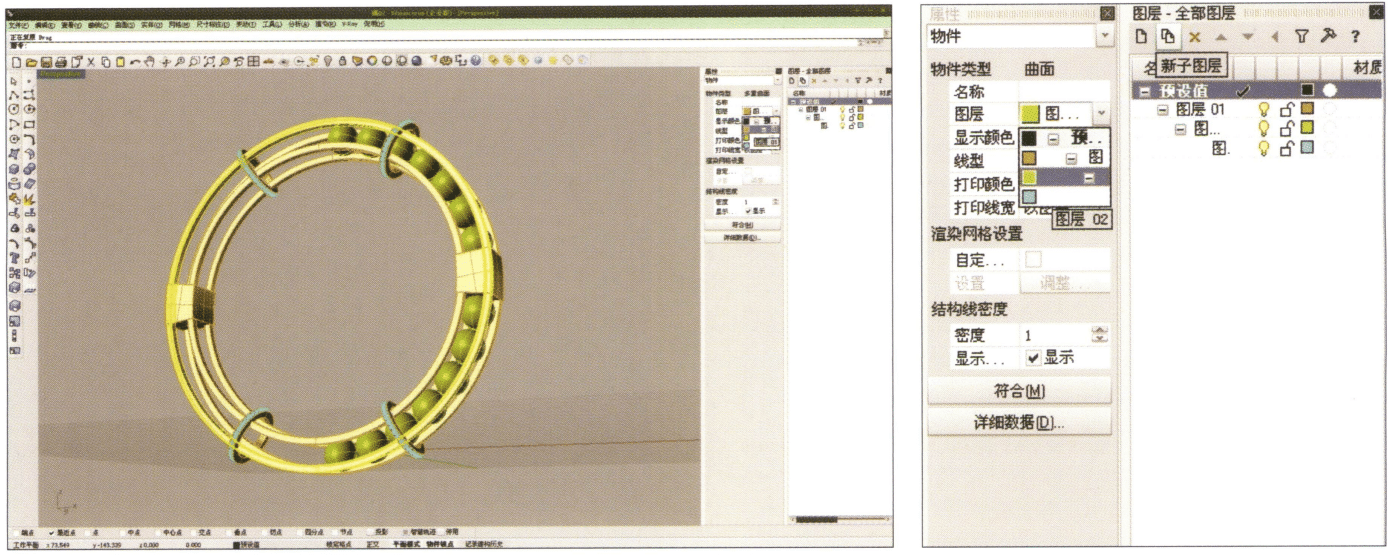
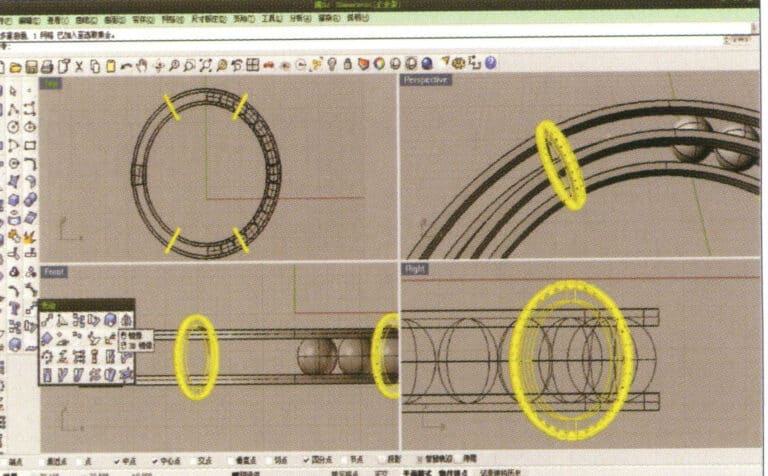
20. Select separately, first create a new layer in the "Layers" window on the right, then select the parts with the same material in the model, choose color layering in the "Layers" section of the "Properties" window, complete and save
21. Select "rendering software" for rendering, and after opening, directly drag the "rhinoceros model" into the Keyshot workspace
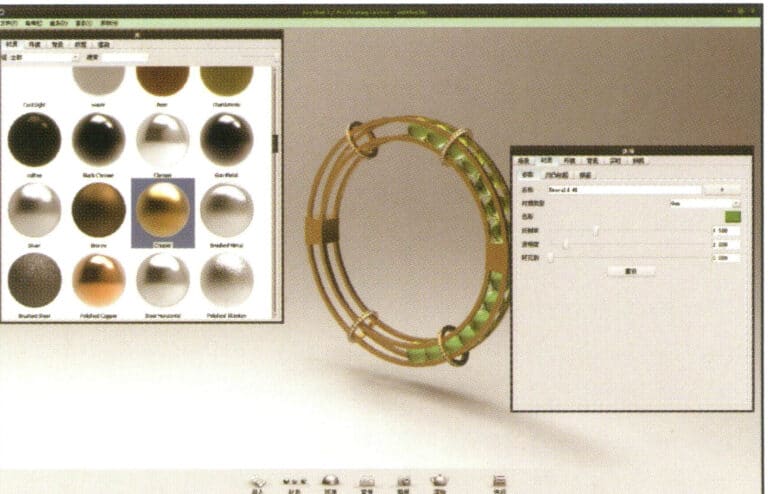
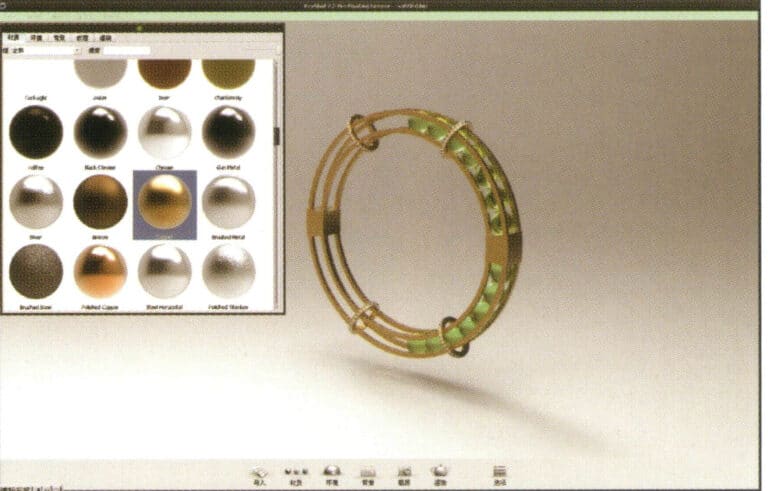
22. Open the "Material" library, select the desired material, and drag it directly onto the corresponding model part to start applying it. After completion, you can double-click the model to make detailed adjustments to that part's material
23. After adjusting the village quality, environment, and view, you can choose "render" to adjust the rendering quality

24. Rendering completed
Section II Aesthetic Review of Digital Paintings

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: 3ds max; The scene applied HDR textures to simulate real natural lighting and set up realistic sunlight; The image shows the object reflecting the red effect of real sunlight
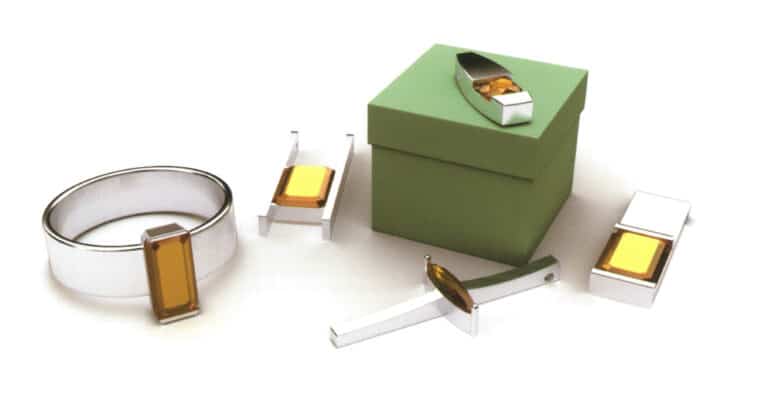

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: 3ds max; The image simulates the effect of natural lighting, setting up the skylight, as if on open ground, influenced only by the environment of the ground and the effect of the skylight
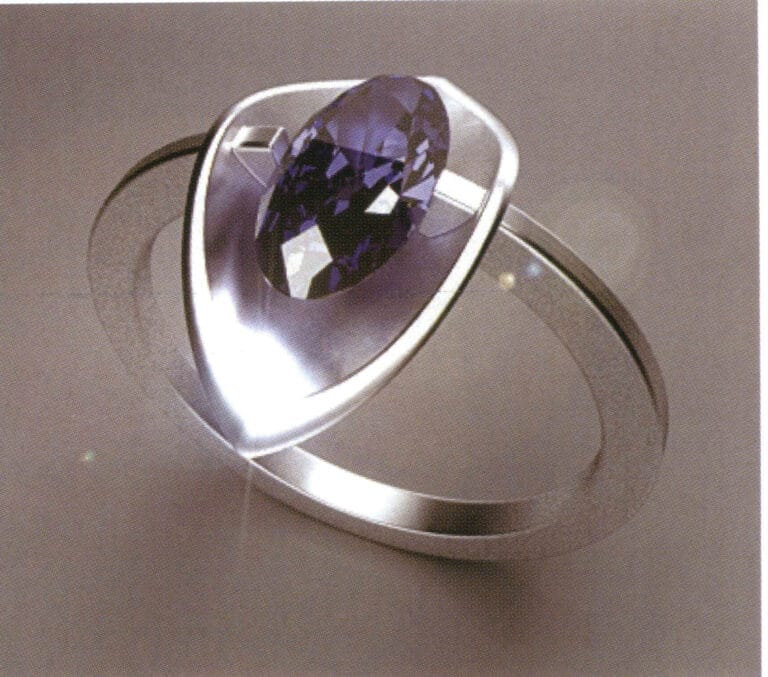

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: 3ds max; The scene uses only one high-intensity surface light source, and the texture of the gemstones is presented quite ideally; due to the high-intensity reflection of the metal surface, the coarse particles on the ground are also reflected on the metal surface
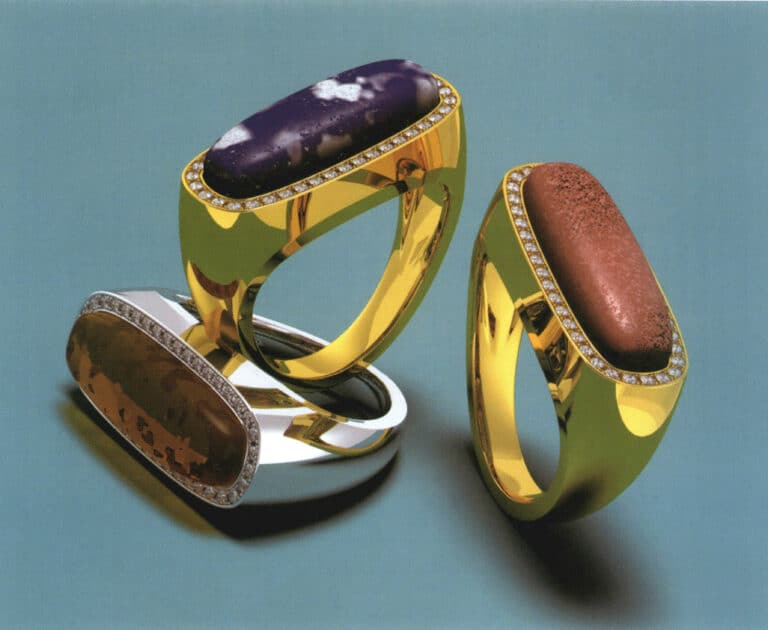

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: Flamingo; Rich organic village textures (amber, coral, lapis lazuli)

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: 3ds max; Simulating natural daylight and adding depth of field effects to mimic the perspective visual effects in real life; The implementation of depth of field relatively extended the rendering time
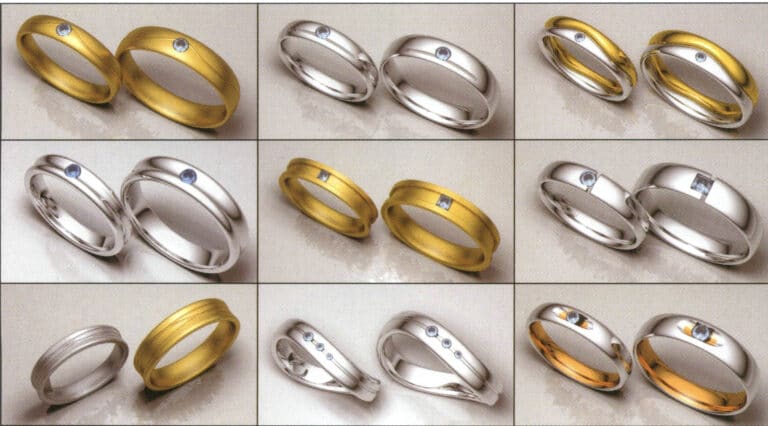

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: Flamingo; Rendering of the wedding ring, different colored metal materials, special matte effect, observing the changes in light absorption and environmental reflection on the metal surface
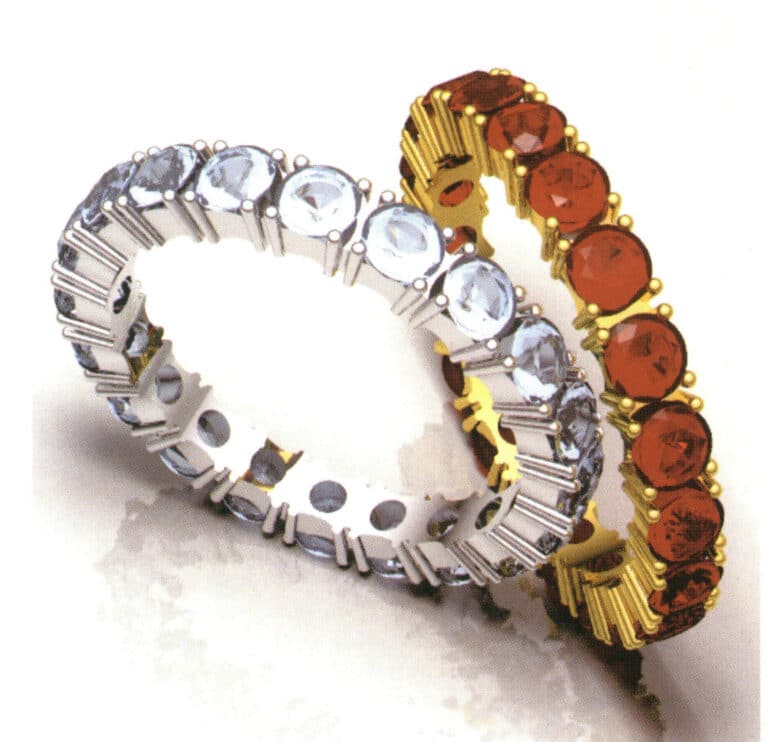

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: Flamingo; Reasonably matches materials and renders the corresponding effects; Has the transparency effect of gemstone material

Modeling: Rhino; Rendering: Flamingo; The higher the quality of the NURBS surface of the object, the finer the image. Every detail must be strictly controlled during the modeling process.
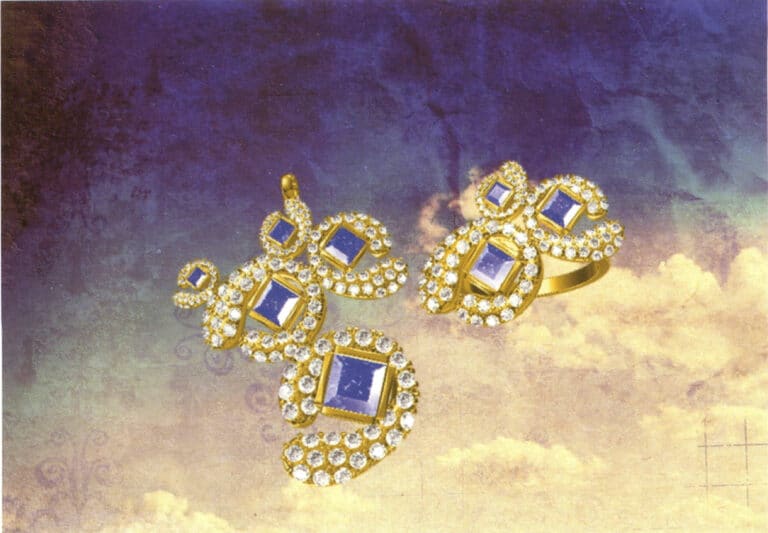

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; During the modeling process, pay attention to the angles and gaps between the repeated arrangement of components and enhance the texture of the metal and gemstones in post-processing
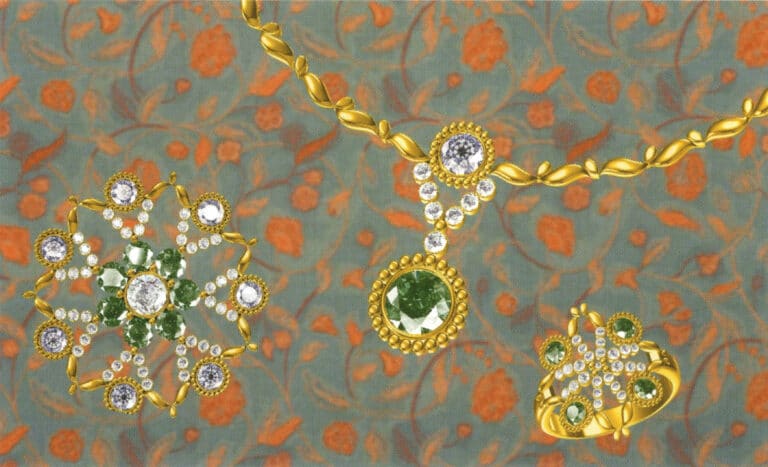

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; During the modeling process, attention should be paid to the variation in the curvature of cluster-set diamonds to ensure it is consistent with the curvature of the gemstones, as well as the connection between the metal parts of different setting methods
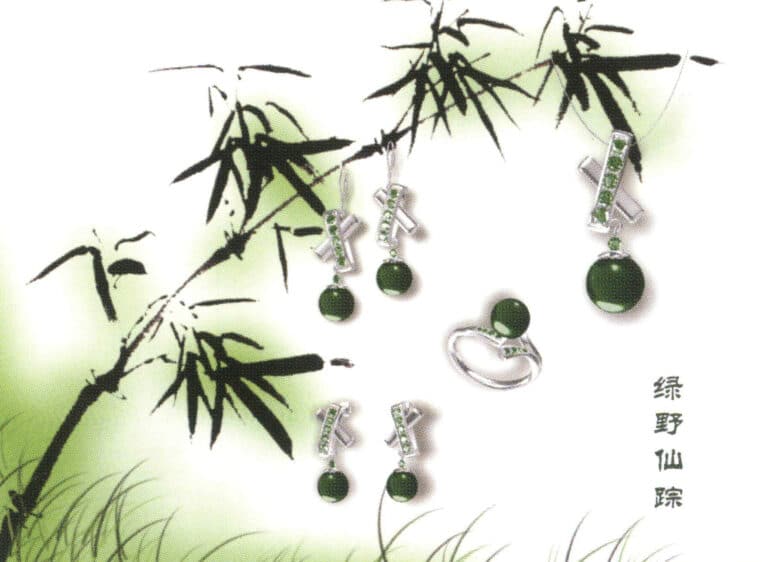

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop. In the modeling process, we have to take into account the matching between the metal material and the gemstone material so that the whole design work has a better visual effect.

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; Pay attention to the change of light and shadow of the metal material, which can help to better express the sense of volume of the jewelry.

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; For more layers of jewelry, pay attention to the connection between the parts in the modeling process, which must be strictly in accordance with the structure of the jewelry to complete the metal part of the processing should pay attention to the changes in light and shadow
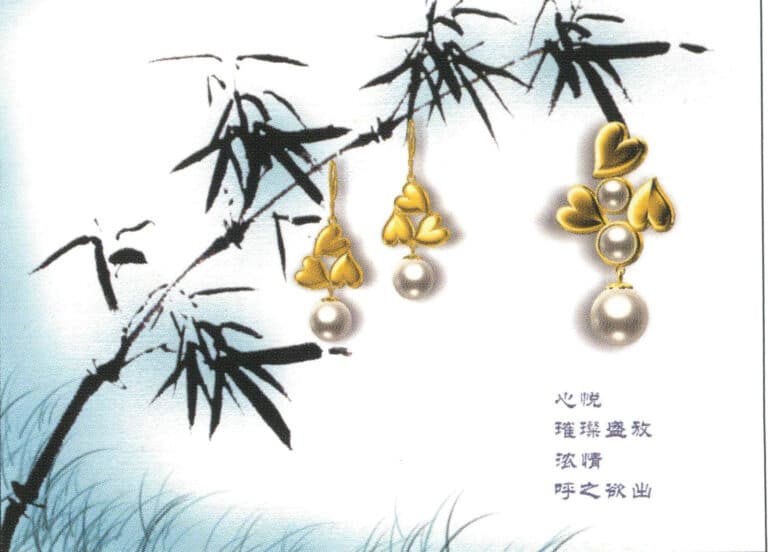

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; Selection of gemstone materials need to take into account the final modeling effect, pay attention to the contrast between light and dark metal and gemstone relations

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; For the representation of different metals, to fully reflect the color and texture differences of the metal

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop. During the modeling process, attention should be paid to the fullness of the shape, and the combination of different colored gemstones should be applied to present a rich color effect.
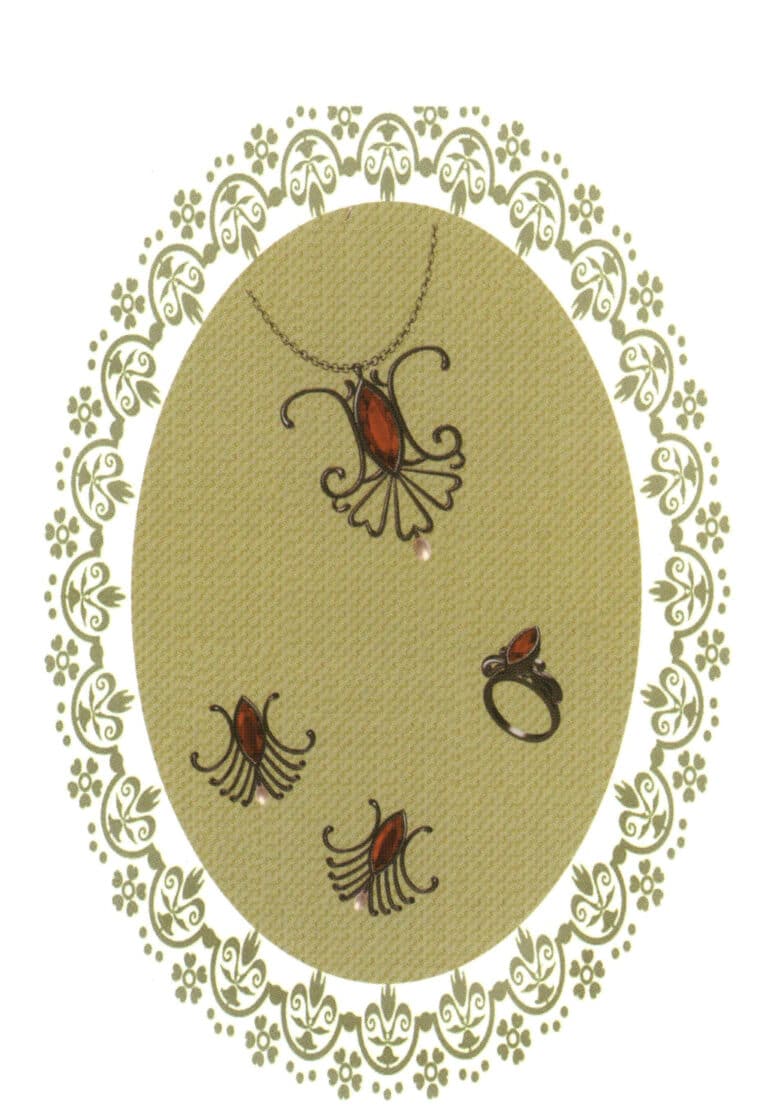

Modeling: JewelCAD; Post-processing: Photoshop; During the modeling process, pay attention to the smoothness of the guide rails and the connection of different section profiles, making the design work natural and comfortable