Mitől lesz az ékszer elbűvölő: Ékszerkészítéshez használt nemes- és közönséges fémek anyaga: Ékszerkészítéshez használt nemes- és közönséges fémek
A Deep Dive into the World of Precious and Common Metals in Jewelry Making
In the vast universe, there are countless types of metals. We are familiar with the types of metals commonly used in jewelry design and production. They have been meticulously selected and forged by craftsmen over the years, making them very suitable for jewelry. As the saying goes, “Each profession has its expertise.” What kind of metal properties should be the first choice for jewelry design and production? Next, we will introduce the metal members of the “jewelry family.”

Közös karátos arany színskála
Tartalomjegyzék
Section I Precious metals of the jewelry family
1. Precious metals and their classification
Precious metals generally include gold, silver, platinum, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, and iridium, totaling eight types.
When we think of the word “precious,” the first association is “expensive.” So, what characteristics must a metal be called a “precious metal”? Below are several characteristics of precious metals summarized for everyone.
(1) Things are valuable because they are rare. Precious metal elements are scarce on Earth, and their distribution is dispersed. The formation of precious metal deposits is difficult, making mining, ore selection, and refining challenging. As a result, various costs rise, and prices naturally become expensive.
(2) Precious metals have very stable chemical properties, making them ideal materials for jewelry making.
(3) Precious metals have unique optical, electrical, and thermal effects, most of which are dazzling and beautiful; they also exhibit good performance under specific conditions and are often used in cutting-edge technology fields of modern science.
(4) Good If metal is beautiful and stable but isn’t easy to reshape, it cannot be used in jewelry design and production. So the precious metals of the jewelry family have very good thermal processing performance; most of them have excellent elasticity, can be pulled into very fine wire and pressed into very thin pieces, but also can be cast in a variety of forms to be able to present the excellent jewelry design well.
2. Common jewelry family precious metals
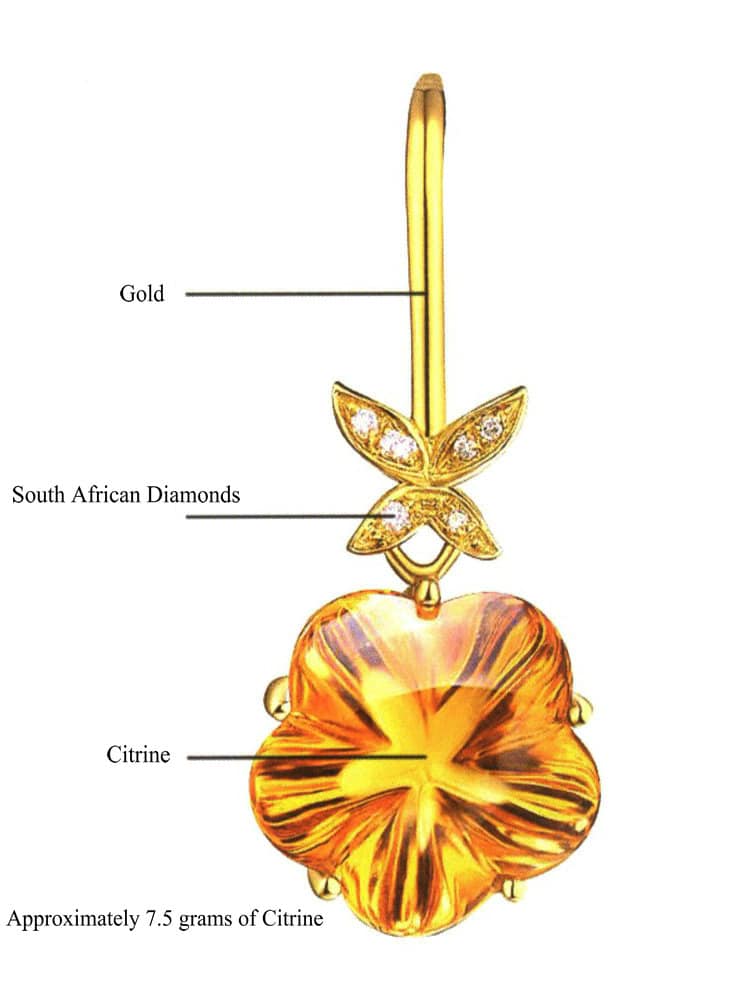
(1) Gold
Chemical element symbol: Au; Atomic number: 79; Melting point: 1064℃; Boiling point: 2880℃; Mohs hardness: 2.5.
The melting point of gold decreases when alloyed with elements like silver and copper. In producing gold jewelry, to avoid damaging the main design during welding, it is generally recommended to use gold with a purity of 90% ~ 95% or silver as solder to lower the melting point, thus preventing damage to the main design during welding.
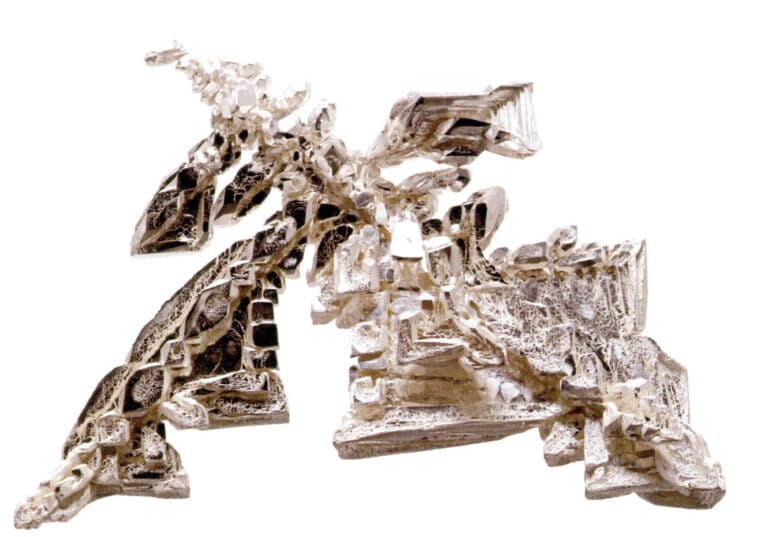
Gold has a high density but low hardness, with a Mohs hardness of only 2.5 (the highest Mohs hardness is 10), which is close to the hardness of human nails. Therefore, gold jewelry may leave scratches after contact with hard objects, resulting in weight loss.

Gold crystals

Ancient gold coins
![[Shang] Bronze human head with a gold mask, unearthed from Sanxingdui, Guanghan, Sichuan](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-16_副本2-768x1178.jpg)
[Shang] Bronze human head with a gold mask, unearthed from Sanxingdui, Guanghan, Sichuan
Gold has great ductility and good malleability, which are excellent characteristics as a member of the jewelry metal family. Gold can be hammered into extremely thin gold leaf and drawn into very fine gold wire using drawing boards and machines; typically, 1 g of gold can be drawn into 320 m of gold wire, and with modern mechanized technology, it can be extended to 3420 m. The national treasure-level artifact we are familiar with, the gold-threaded jade garment unearthed in Mancheng, Hebei, was woven from gold wire with a diameter of 0.08~0.14 mm, demonstrating that the excellent properties of gold were well discovered and utilized in ancient times.
Gold has good thermal and electrical conductivity, second only to silver, and has a dazzling golden metallic luster. Throughout history, gold has been loved by people worldwide, whether in the East or the West, and many precious cultural relics and artworks feature gold products.
(2) Silver
Chemical element symbol: Ag; atomic number: 47; melting point: 961.93℃; boiling point: 2210 ℃; Mohs hardness: 2.7.
Silver has the best electrical conductivity among all metals, and its thermal conductivity is also excellent. Additionally, silver has good elasticity, second only to gold. Using modern technology, 1 g of silver can be drawn into fine wire of 1800~2000 m and wrapped into silver foil that is 0.025 mm thick, making it very convenient for jewelry design and production. Moreover, silver has a relatively low melting point. Silver generally emits a pure white and pleasing metallic luster, with a reflectivity of up to 94%, making it the closest precious metal to pure white.
The chemical properties of silver are relatively stable; it does not react with oxygen at room temperature, and its color remains unchanged in the air. However, compared to gold, it is still considered an easily oxidizable metal, forming black silver oxide upon oxidation. When silver comes into contact with sulfur-containing substances or is exposed to gases containing sulfur dioxide or hydrogen sulfide, it will react with sulfur to form black silver sulfide. Silver can also react with arsenic to form black silver arsenide, which has historically been used to test whether food contains arsenic (arsenic oxide).
Silver products sold on the market undergo plating processes to make silver less prone to oxidation, usually plated with nickel or gold; silver tableware generally does not require plating, only regular cleaning and maintenance. No electroplated silver products are placed in the air for a long time or worn after not often cleaned up; the surface may produce a black layer. You can use a clean silver polishing cloth to wipe or a soft cotton cloth smeared with toothpaste to wipe, and then rinse with water; the black layer will generally disappear, but it is also available to clean up the professional silver washing water to reduce the loss of the surface of the ornaments.
As a member of the jewelry metal family, silver has excellent properties and a very beautiful appearance, making it very popular. Many jewelry pieces are made from silver, and China is also a major consumer of silver.

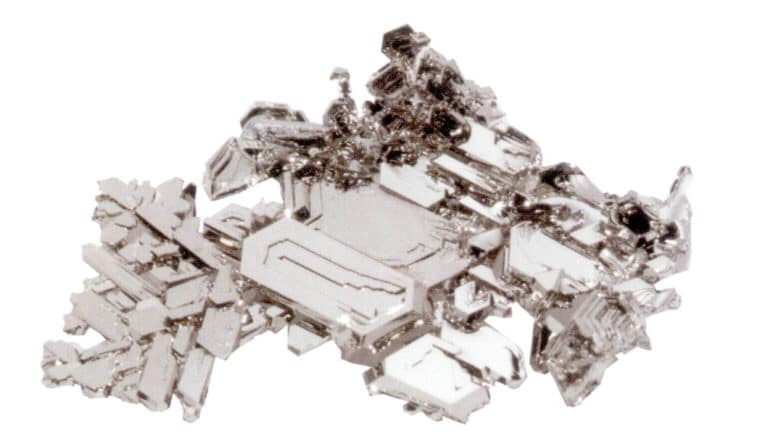
Ezüst

Full Silver 999 Bar
(3) Platinum Group Elements
The known platinum group chemical elements are ruthenium (Ru), rhodium (Rh), palladium (Pd), osmium (Os), iridium (Ir), and platinum (Pt). Platinum group elements are rare elements, and their common characteristics include high melting points, high boiling points, oxidation resistance, and corrosion resistance. Due to the high reflectivity of platinum group metals to visible light, they are all silver-white or steel-white in color and have good flexibility. The platinum group elements commonly used in jewelry design and production are platinum and palladium.
① Platinum
Chemical element symbol: Pt; Atomic number: 78; Melting point: 1769℃; Boiling point: 3827℃; Mohs hardness: 4.3.
Platinum has the highest density among jewelry metals, with a gray-white metallic luster, bright color, good electrical conductivity, and flexibility. Its flexibility is close to that of silver and gold, and it can be wrapped into platinum foil as thin as 0.001 mm and drawn into wires with a diameter of 0.001 mm. Platinum is also quite expensive, and many precious gemstones often choose platinum for setting.
② Palladium
Chemical element symbol: Pd; Atomic number: 46; Melting point: 1550℃; Boiling point: 3127℃; Mohs hardness: 4 〜4.5.
Palladium has a silvery-white metallic luster, resembling platinum in appearance, with good electrical and thermal conductivity. Its chemical properties are relatively stable, and it is not easily oxidized in the air at room temperature. However, palladium is the least corrosion-resistant metal among the platinum group metals, as it can be dissolved by nitric acid, hot sulfuric acid, and others.

Section II Classification of Precious Metal Jewelry and Interpretation of Marks
In the previous section, we learned about precious metals commonly used in the jewelry family. Due to their rarity, value, stable performance, resistance to corrosion, dazzling beautiful metallic luster, and malleability for easy processing, they have been used to make ornaments since ancient times. We classify precious metal jewelry into gold, silver, platinum, and palladium jewelry based on the materials.
![[GREECE] Wristband, gold, penannular, 800-1000](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-20_副本-768x382.jpg)
The once-familiar names in the Chinese precious metal product market, such as “thousand solid gold” and “ten-thousand solid gold,” have become a thing of the past, with “pure (gold, platinum, palladium, silver)” defined as the highest purity of jewelry products, indicating that the precious metal content is not less than 990‰. The purity is expressed as the minimum value without negative tolerance. The standard modification regulates the naming of purity and does not restrict the production and sale of jewelry products with precious metal content reaching 999‰, 999.9‰, or more.
![[Greece] Golden Horse Earring, 5th-3rd century B.C.](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-20_副本1-768x999.jpg)
[Greece] Golden Horse Earring, 5th-3rd century B.C.
![[Egypt] Gold finger ring, 1st century A.D.](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-20_副本2-768x978.jpg)
[Egypt] Gold finger ring, 1st century A.D.
1. Gold jewelry
The purity and material mark representation method for gold jewelry is the purity thousandths (K number) and a combination of gold, Au, or G. For example, gold 750 (18K gold), Au750 (Au18K), and G750 (G18K). The purity of gold content not lower than 990‰ is marked as “pure gold.”
(1) Pure gold (gold content not lower than 990‰)
Our country’s official jewelry mark for pure gold jewelry is “pure gold.” Suppose you want to inform consumers of the detailed gold content. In that case, you can also label the content on the jewelry, such as pure gold with a gold content not lower than 990‰, marked as “manufacturer code + pure gold” or “manufacturer code + pure gold 990”; pure gold with a gold content not lower than 999‰, marked as “manufacturer code + pure gold 999”; pure gold with a gold content not lower than 999.9‰, marked as “manufacturer code + pure gold 999.9,” etc.

Pure gold jewelry has a high gold content and a golden color and is deeply loved in China and among Chinese communities, accounting for a significant portion of consumption. This is because it can serve as decoration and a means of value preservation. The drawbacks of pure gold jewelry are its low hardness, susceptibility to wear, and difficulty maintaining fine patterns. With the gradual improvement and enhancement of jewelry processing techniques, there are now pure gold products made with 3D and 5D hard gold technology, which can make pure gold thinner, hollow in the middle, and with a certain increase in hardness, allowing for the creation of larger jewelry pieces with a small amount of gold. In recent years, these have become very popular among the public.

(2) Gold alloy ( K gold)
To overcome the disadvantages of pure gold jewelry, such as poor hardness, single color, easy wear, and lack of detailed shapes and patterns, people have gradually researched gold alloy jewelry, marked with purity in Karat, forming the most common series today—K gold jewelry. Gold jewelry uses less gold, has lower costs, and can be made in various colors, with hardness higher than pure gold, making it less prone to deformation and wear, especially when used for gemstone inlays, which are firm and beautiful. These advantages have allowed gold jewelry to quickly occupy a large market. K gold has a gold content of 1000‰ for 24K gold. However, 24K gold is only a theoretical value, and actual operations cannot achieve it, so some 24K gold jewelry on the market does not meet standard regulations.

Oraik, Jaguar, 22K Gold Ring

Oraik, Magic Runner, 22K Gold Ring
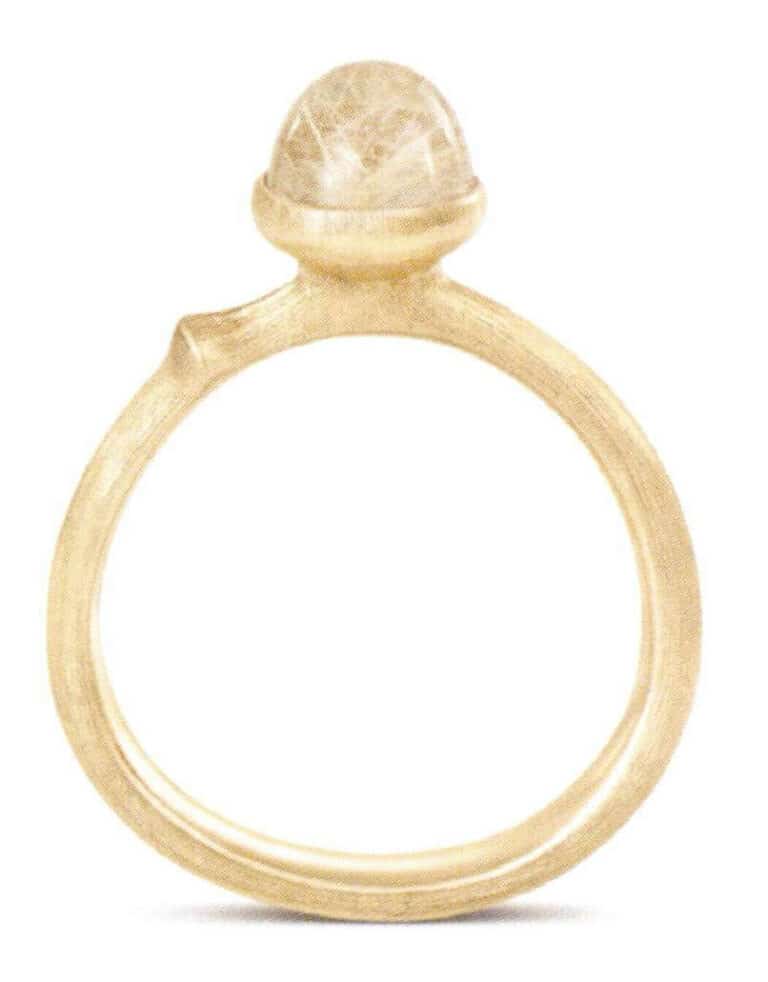

Ole Lynggaard Copenhagen, 18K Gold Ring
- 22K gold (gold content not less than 916‰): marked as gold 916 (22K gold), Au916 (Au 22K), G916 (G22K). In Europe, 22K gold is standard gold, commonly used for wedding rings and gold coins.
- 18K gold (gold content not less than 750‰): marked as gold 750 (18K gold), Au750 (Au18K), G750 (G18K). 18K gold has moderate hardness and ideal ductility, with soft edges that are not easily deformed or broken, making it suitable for setting various gemstones. Jewelry with exquisitely detailed textures is often made from 18K gold, as it can present the design more delicately.
- 14K gold (gold content not less than 585‰): marked as gold 585 (14K gold), Au585 (Au14K), G585 (G14K).
- 9K gold (gold content not less than 375‰): 9K gold is generally used to make high-end items such as lighter cases, gold pen barrels, and powder boxes. There are also some trendy light luxury accessories made from 9K gold in the market, which are popular among young consumers due to their affordable prices and novel styles.
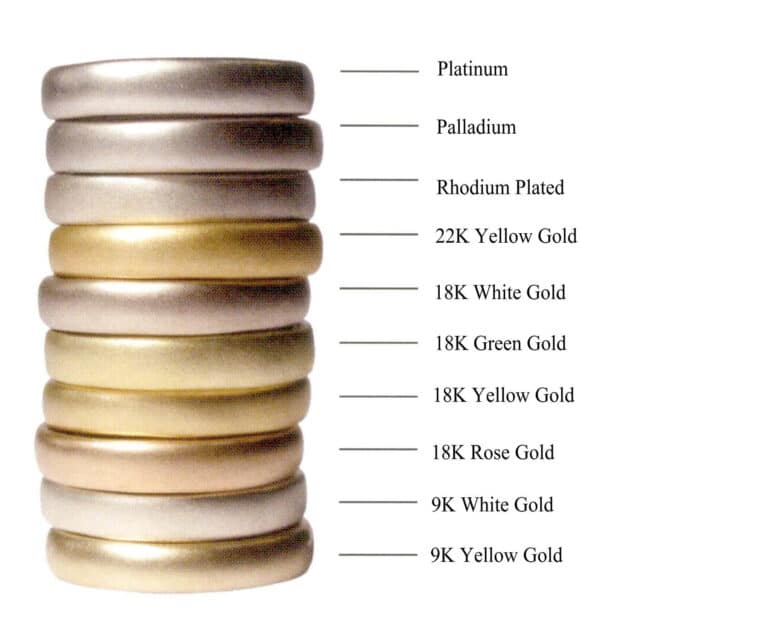
Common karat gold ratio, melting point, specific gravity table
| Termék neve | Gold: alloy ratio | Olvadáspont | Fajlagos tömeg |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 K Gold | 24 : 0 | 1063℃ (1945°F) | 19.32 |
| 22K Gold | 22 : 2 | 940℃(1724°F) | 17.2 |
| 18 K Gold | 18 : 6 | 904℃(1660°F) | 16.15 |
| 14 K Gold | 14 : 10 | 802℃(1476°F) | 13.4 |
| 9 K Gold | 9 : 15 | 880 〜900℃ (1616 〜1652°F) | 11.2 |
- Colored K gold: Designers often feel that the colors of precious metals are limited when creating works, with the common ones being gold and white. Therefore, the emergence of colored K gold creates more jewelry art possibilities. Most colored K gold jewelry uses colored 18K gold. In colored 18K gold, the proportions of components other than 750‰ gold can be adjusted to present different colors.
Red K gold, also known as rose gold—gold, silver, copper can be combined to create red and light red K gold; green K gold, and gold and aluminum make bright red karat gold—adding a small amount of cadmium to the gold, silver, and copper alloy can produce green K gold; blue K gold—adding cobalt to the surface of a gold and iron alloy can achieve this; white K gold—adding nickel or palladium to a gold-copper alloy can produce this; black K gold—adding a high concentration of iron to gold can achieve this, with the black 14K gold ratio being gold 58.3%, iron 41.7%.
Some colored K gold is made using surface plating rather than smelting, making the color prone to wear. Some white 18K gold on the market is made by plating nickel or rhodium, with palladium on the surface of 18K gold. After wear, the jewelry turns yellow, revealing the original color of 18K gold. Therefore, it is necessary to consult the supplier clearly when purchasing to avoid making a wrong choice.

Közös karátos arany színskála

Nacreous 18k Rose Gold / White Gold Bracelet Tasaki
2. Silver Jewelry
Silver is white, has a delicate and flexible texture, is easy to process, and has a price much lower than gold, making it an important component of jewelry-making materials since ancient times. Silver jewelry’s purity and material mark are indicated by the purity fraction and a combination of silver, Ag, or S. For example, silver 925, Ag925, and S925.
(1) Pure Silver (silver content not less than 990‰)
Marked as “Pure Silver,” if you want to inform consumers of the detailed silver content, you can also label it on the jewelry, such as pure silver with a silver content not less than 990‰, marked as “Manufacturer Code + Pure Silver” or “Manufacturer Code + Pure Silver 990”; pure silver with a silver content not less than 999‰, marked as “Manufacturer Code + Pure Silver 999”; pure silver with a silver content not less than 999.9‰, marked as “Manufacturer Code + Pure Silver 999.9.” Ag990, S990, etc., are also marks of pure silver.
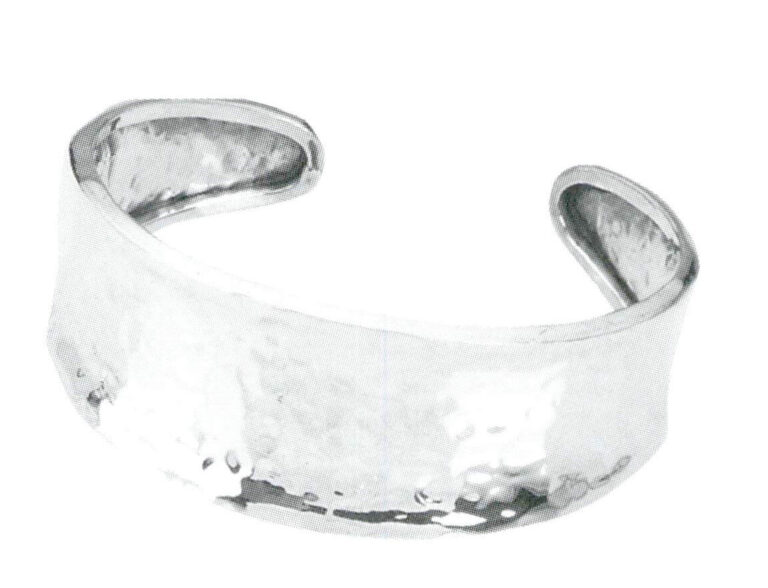

Hammered silver bracelet, fine silver 990

Dragon pot, traditional engraving, pure silver 990
(2) Silver 925 (silver content not less than 925‰)
Marked as silver 925, Ag925, or S925. The popular cast silver jewelry on the market often uses silver 925 because it is harder than pure silver, making it less prone to deformation and wear, which is better for creating relatively intricate jewelry styles. If it is traditional engraved silver jewelry, pure silver is often used because it is softer, making it easier to repeatedly hammer, engrave, and process.
(3) Silver 800 (silver content not less than 800‰)
Marked as silver 800, Ag800, S800.

Silver 925 Earrings

Stellar Jewellery, Silver 925 Brooch
Copywrite @ Sobling.Jewelry - Egyedi ékszergyártó, OEM és ODM ékszergyár
3. Platinum Standard
Platinum is commonly known as white gold. The purity and material mark of platinum jewelry is indicated by a purity fraction and a combination of platinum (platinum, white gold) or Pt. For example, platinum (platinum, white gold) 900, Pt900.
(1) Pure platinum (platinum content not less than 990‰)
Marked as “Pure Platinum”. The specific content of precious metals can also be indicated on the jewelry, such as pure platinum with a platinum content not less than 990‰, marked as “Manufacturer Code + Pure Platinum” or “Manufacturer Code + Pure Platinum 990” or “Manufacturer Code + Pt990”; pure platinum with a platinum content not less than 999%, marked as “Manufacturer Code + Pure Platinum 999” or “Manufacturer Code + Pt999”

Earrings in platinum with gemstones, ART DECO period

Platinum diamond ring collection
(2) Platinum 950 (platinum content not less than 950‰)
Marked as platinum 950 or Pt950.
(3) Platinum 900 (platinum content not less than 900‰)
Marked as platinum 900 or Pt900.
The strength of platinum 900 is appropriate, and it is used more frequently in jewelry, especially in set jewelry, where platinum 900 is commonly used for its firmness and resistance to falling off. When setting wedding rings, platinum 900 or platinum 950 is often used; however, for jewelry that uses more gold, white 18k gold is generally used to replace platinum because platinum has a higher density than gold, making it relatively heavier for the same volume. Considering both comfort and value retention, white 18K gold is a relatively cost-effective choice.
(4) Platinum 850 (platinum content not less than 850‰)
Marked as platinum 850 or Pt850.
4. Palladium Jewelry
In jewelry, palladium often appears as an alloying element in platinum, palladium alloys, or white K gold. Adding palladium to platinum can improve its casting performance and surface quality. The market share of palladium jewelry in our country is relatively small, but with the development of the domestic jewelry industry, some companies have recently joined the production of palladium jewelry, considered a relatively niche precious metal jewelry. The purity and material stamp of palladium jewelry is expressed as a combination of purity in thousands and palladium (Pd) or Pd. For example, palladium (palladium) 950, Pd950.
(1) Pure palladium (palladium content at least 990‰).
Marked as “pure palladium.” At the same time, the specific content of precious metals can be indicated on the jewelry, such as palladium content of not less than 990%. Pure palladium is marked as “manufacturer code + Pure palladium,” “manufacturer code + Pure palladium 990,” or “manufacturer code + Pd990”; pure palladium with a palladium content not less than 999‰ is marked as “manufacturer code + Pure palladium 999” or “manufacturer code + Pd999.”
(2) Palladium 950 (palladium content not less than 950‰).
Marked as palladium 950 or Pd950.
(3) Palladium 900 (palladium content not less than 900‰)
Marked as Palladium 900 or Pd900.
(4) Palladium 500 (palladium content not less than 500‰)
Marked as Palladium 500 or Pd500.
Jewelry is generally divided into two main parts: the main body and the accessories. For example, the clasp part of a necklace or bracelet belongs to the accessories. Due to the requirements of strength and elasticity, the gold content of the accessories differs from that of the main body, but the materials must also meet national standards, such as gold jewelry with a gold content of no less than 916‰; the gold content of its accessories must not be less than 900‰; platinum jewelry with a platinum content of no less than 950‰; the platinum content of its accessories must not be less than 900‰; palladium jewelry with a palladium content of no less than 950‰%; the palladium content of its accessories must not be less than 900‰; and sterling silver jewelry, where the silver content of its accessories must not be less than 925‰.
5. Precious metal-coated jewelry
(1) Wrapped gold, wrapped silver, etc.
① Manufacturing method:
The method of mechanically processing to securely wrap gold foil around the jewelry to obtain a metal coating is called gold plating. Silver plating is the same method used to wrap silver around the jewelry. In addition, using rolling and forging techniques to press alloy gold foil onto the surface of other metals to make jewelry is called forged gold jewelry, a type of gold-plated jewelry.
② Quality inspection specifications:
The gold content of the gold-plated layer must not be less than 375‰, and the thickness must not be less than 0.5μm. In our country, it is marked as L — Au; abroad, it is marked as 14KF, 18 KF. The silver content of the silver-plated layer must not be less than 925‰, and the thickness must not be less than 2μm, marked as L- Ag.

(2) Gold plating, silver plating, etc.
① Production method:
The gold coating obtained by electroplating or chemical plating is called a gold coating. Similarly, there are silver coatings, rhodium coatings, etc.
② Quality inspection specifications:
The gold content of the gold coating must not be less than 585‰, and the thickness must not be less than 0.5μm. , marked as P — Au. The silver content of the silver coating must not be less than 925‰, and the thickness must not be less than 2μm, marked as P — Ag.

Yu Peini, variable—2 necklace, copper gold-plated

Gold doll ice cream, earrings, silver 925 color gold-plated
(3) Gilding
In ancient times, gold was dissolved in mercury and then brushed onto the surface of objects. After drying, it was baked with charcoal to evaporate the mercury, and the method of polishing the surface with agate was called gilding. Nowadays, apart from restoring old items or making antique-style ornaments, the gilding technique is rarely used to mass-produce commercial jewelry.
![[Ming] Manjushri, gilt-bronze statue](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-29_副本-768x926.jpg)
[Ming] Manjushri, gilt-bronze statue
![[Qing Dynasty] Gilt-silver inlaid beads and stone fingernail set](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-29_副本1-768x1104.jpg)
[Qing Dynasty] Gilt-silver inlaid beads and stone fingernail set
![[Eastern Han Dynasty] Gilt inlaid beast inkstone case](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-29_副本2-768x460.jpg)
[Eastern Han Dynasty] Gilt inlaid beast inkstone case
Section III Common metals used in jewelry making and their classification
During artistic creation or experimentation, relatively inexpensive metals are often used for jewelry design, such as copper, titanium, aluminum, and zinc; these metals can exhibit various colors through electroplating or heat treatment and are also widely used in the design and production of trendy fast-fashion accessories. These types of accessories have novel styles, are updated quickly, and are larger than precious metal jewelry, making common metals more cost-effective. It is important to note that common metals should be stored separately from precious metals to prevent contamination during heating.
1. Copper
Chemical element symbol: Cu; Melting point: 1800℃.
Copper is a light brown metal that can harden quickly when cooled. It is often added to silver and gold to form alloys, enhancing the malleability of silver and gold or giving them different colors. Copper can also be used directly to make jewelry. When copper is annealed, it may turn black and then appear pink, at which point it can be quenched. After quenching, copper becomes soft and easier to shape. Many copper jewelry pieces on the market combine gold plating or gold-filled techniques, which can delay the oxidation of the copper surface and give the copper jewelry a luster similar to gold and silver, making it more beautiful.

Réz
![[Shang] Shang copper vertical eye mask, Sichuan Guanghan San](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-30_副本1-768x778.jpg)
[Shang] Shang copper vertical eye mask, Sichuan Guanghan San
![[Shang] Tiger's human tooth, unearthed from the bronze star mound, bronze](https://sobling.jewelry/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/铜板纸-创饰技金属首饰的制作奥秘-30_副本2-200x300.jpg)
[Shang] Tiger's human tooth, unearthed from the bronze star mound, bronze
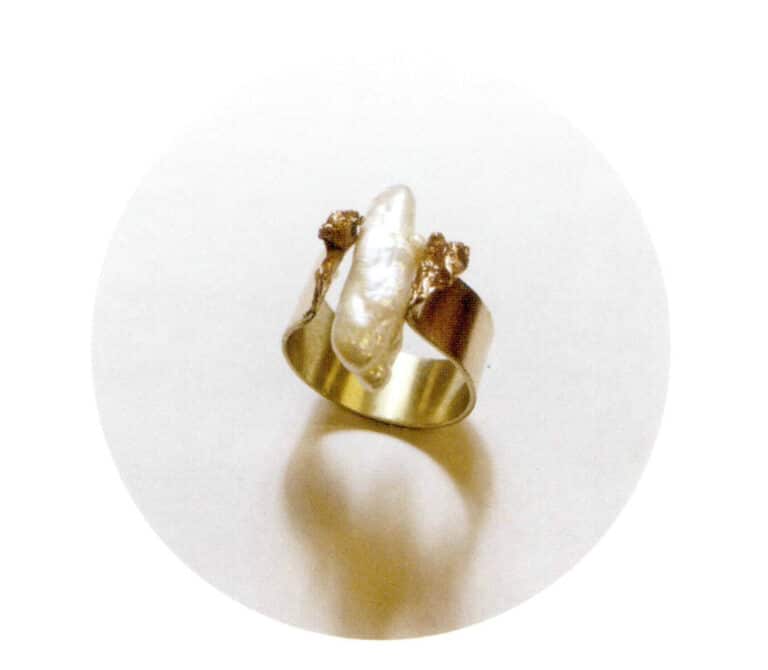

Xiebai, liquid freedom, ring, brass, Baroque pearls, crumpling technique
2. Titanium
Chemical element symbol: Ti; Melting point: 1800℃; Specific gravity: 4.5.
Titanium is a hard but light white metal with a very high melting point, making it unsuitable for welding. However, its lightness makes it suitable for making large pieces of jewelry. Titanium metal can be combined with processes such as electrolysis and anodizing to create various brightly colored and fade-resistant jewelry.
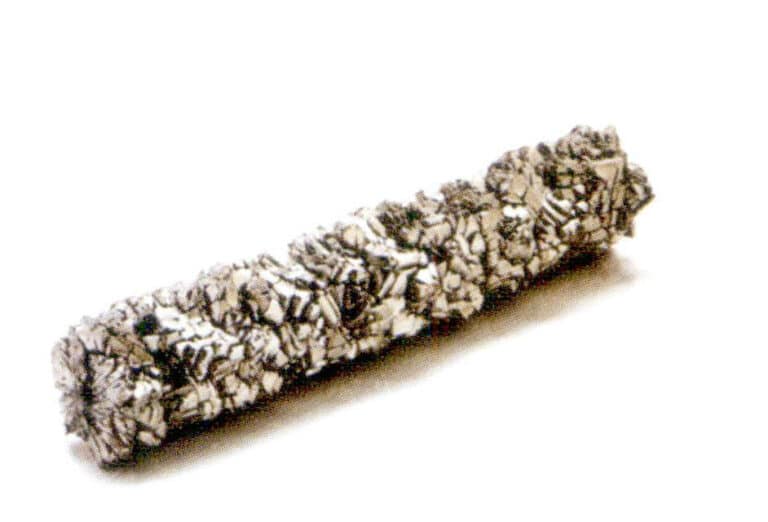

Titanium
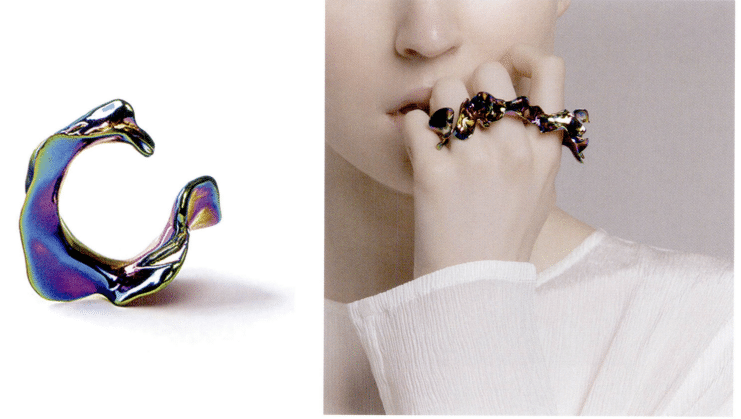

YVM1N Yume, GALAXY Aurora, Titanium

Chen Shiying (Wallace Chan), aquatic, key metal
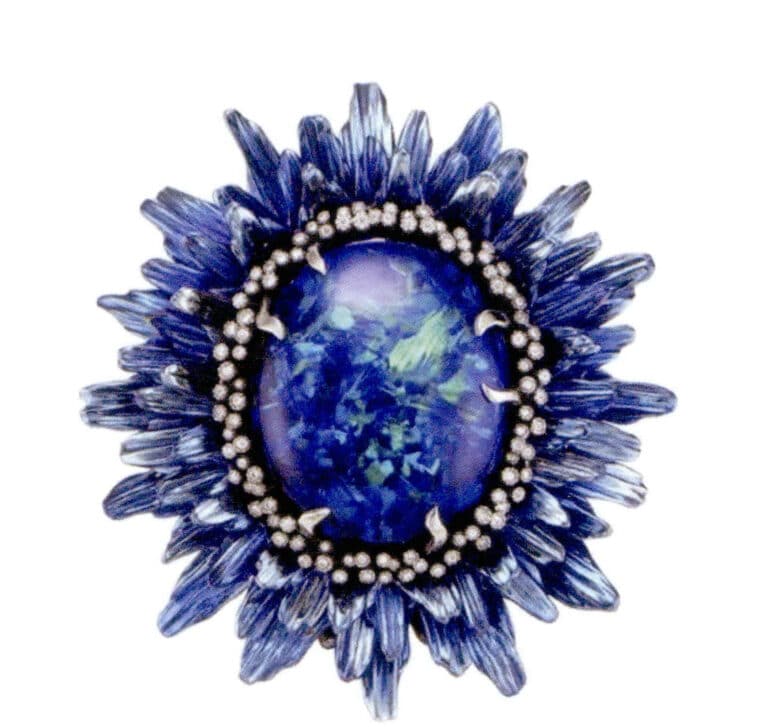

Chopard, Fleurs d'Opales, titanium metal
3. Aluminum
Chemical element symbol: AI; Melting point: 660℃; Specific gravity: 2.7.
Aluminum is a gray metal with a textured surface, is very light in weight, and is easy to cut on a lathe, but it isn’t easy to bend into special shapes and cannot be welded. Currently, aluminum jewelry mainly uses computer numerical control machine tools (CNC) for carving and shaping. Later, it can be treated with anodizing, electroplating, and other processes to present different colors, mostly used for making souvenirs.

Alumínium

Dimond Home, aluminum tray

Jewelry, Aluminum Anodizing Process
Necklace, aluminum spacer anodized
4. Zinc
Chemical element symbol: Zn; Melting point:419℃; Specific gravity: 7.1.
Zinc is a white metal usually used to alloy other metals. It has a low melting point and can also be used as a solder for silver. However, zinc alloys have poorer ductility than copper and are prone to breaking, so they are generally used for fast-fashion jewelry or souvenir accessories that wear out quickly.

Cink

Zinc alloy vintage decorations